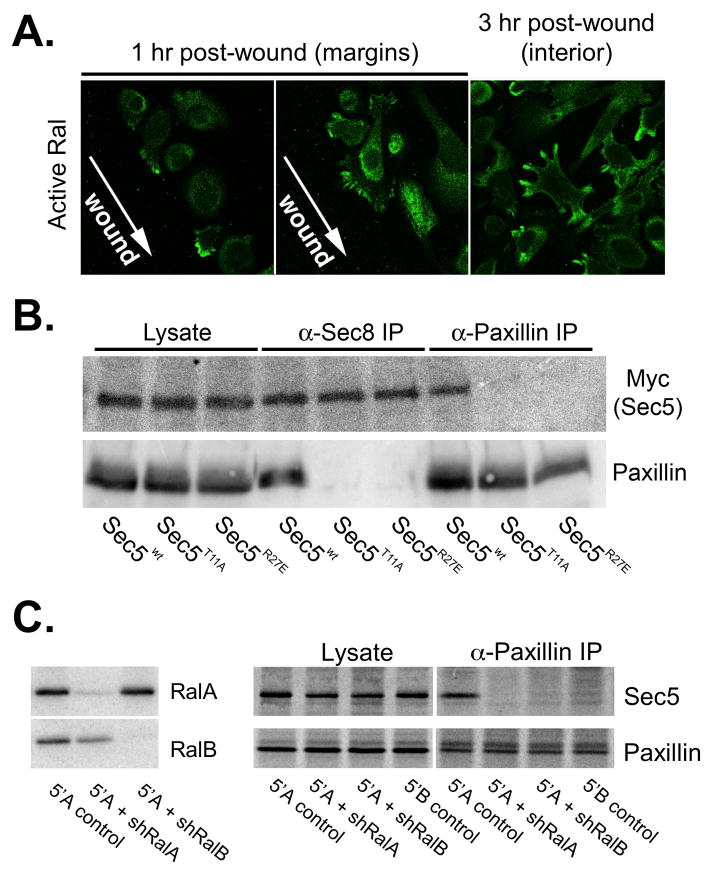
Figure 8. Ral GTPases are required for Exocyst association with paxillin in cells.
(A) Localization of active Ral following wounding of prostatic tumor cells. Cells were transfected with X-Press-tagged Exo84 Ral-binding domain and monolayers were wounded by scratching. Active Ral GTPase localization was determined by immunofluorescence staining with anti-X-Press antibodies at indicated time points. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of Exocyst and paxillin is dependent on Ral-binding capability of Sec5. Cells were transfected with plasmids encoding myc-tagged Sec5 (wild type (wt) or Ral-uncoupled mutants (T11A or R27E)). Cells were extracted in 1% Triton X-100 and extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with antibodies to Sec8 or paxillin. Presence ectopic myc-Sec5 and paxillin in equivalent amounts of whole cell extracts (“lysate”) and precipitated immune complexes was assessed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. (C) RNAi mediated reduction of RalA and RalB expression. R3327-5′A were infected with recombinant lentiviruses coding shRNAs specific for RalA or RalB. Stable clones of cells were selected in puromycin and assessed for RalA and RalB expression by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. (D) R3327-5′B, R3327–5′A or R3327–5′A cells expressing shRNAs targeting RalA or RalB were extracted in 1% Triton X-100. Extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with antibody to paxillin. Presence Sec5 and paxillin in equivalent amounts of whole cell extracts (“lysate”) and precipitated immune complexes (“α-paxillin IP”) was assessed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with specific antibodies.