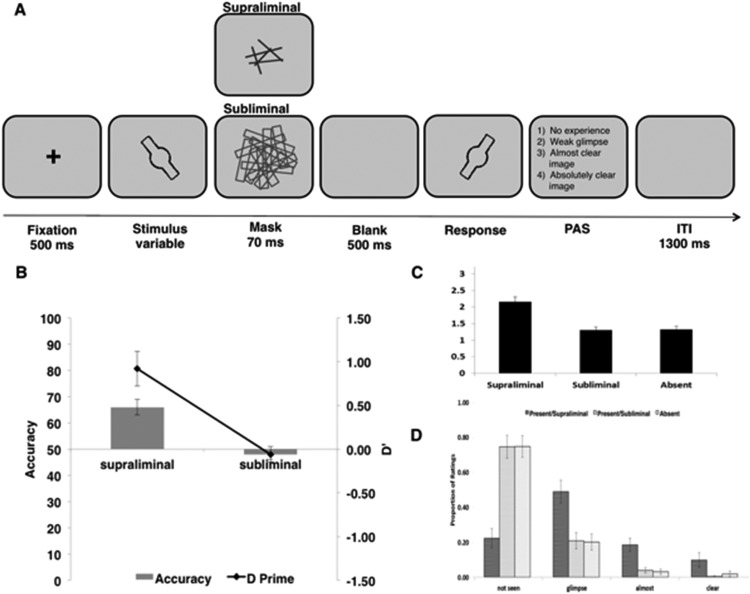
Figure 2.
Design of the visual identification task used in Experiments 1a and 1b, and results of the visual identification task in Experiment 1a. (A) A central fixation cross was presented for 500 ms followed by a 16-ms prime stimulus (present on 50% of trials, blank shown on other 50% of trials), and then a 70-ms dense or sparse backward mask. After a 50-ms mask-probe interval, a probe stimulus (congruent or incongruent with the prime stimulus) appeared for 100 ms. Participants first completed a forced-choice discrimination task indicating whether the probe was of the same or different orientation as the stimulus. Next, participants rated their subjective awareness using the PAS (Ramsøy & Overgaard, 2004). After a 1,300 ms intertrial interval the next trial began. (B) Accuracy and d′ in the forced-choice identification task for the dense and sparse mask condition separately. (C) Mean awareness ratings for the sparse-mask, dense-mask, and stimulus-absent conditions separately. (D) Proportion of different awareness ratings in the identification task for the three conditions. Error bars reflect ±1 standard error.