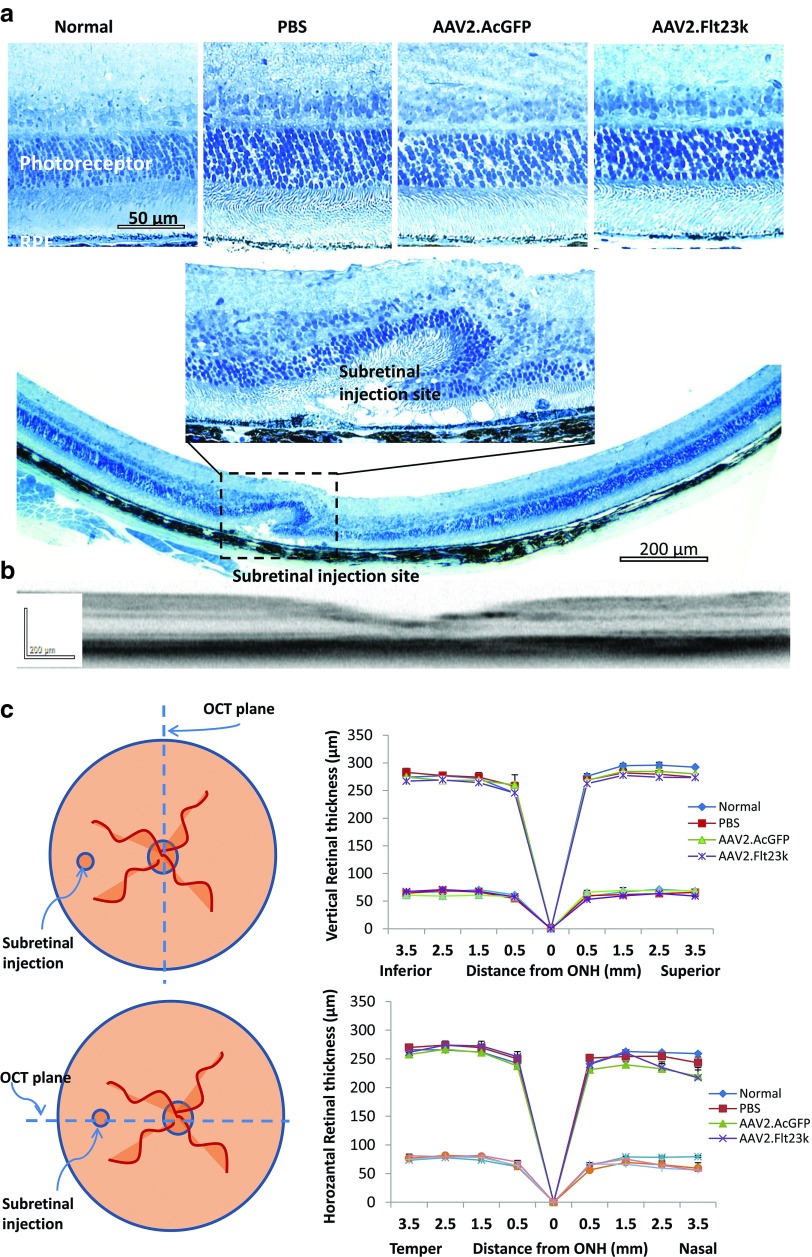
Figure 5.
AAV.Flt23k does not affect retinal thickness. (a) Retinal sections of AAV2.Flt23k treated mice and control mice. Top: High magnification (×40) of normal, control and AAV2.Flt23k treated eye retinal sections shows no toxicity of retinal and outer nuclear layer. Middle: High magnification (×40) of subretinal injection site. In the injection site, the retinal structure was damaged and the outer nuclear cells degenerated. Bottom: The whole retinal section (×10) shows only injection site retinal degeneration, other parts of retina remain normal. (b) Representative optical coherence tomography (OCT) subretinal injection section. The OCT image shows the whole retinal structure is normal except the injection site. (c) Top left: The schematic of method of OCT assesses the retinal thickness along the vertical axle. Top right: The thickness of the whole retina and outer nuclear layer (ONL) in normal C57 mice and mice who received subretinal injection of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), AAV2.AcGFP, or AAV2.Flt23k. In each group, n = 5. The error bar represents the SD. Bottom left: The schematic of method of OCT assesses the retinal thickness along the horizontal axis. Bottom right: The thickness of the whole retina and ONL in normal C57 mice and mice who received subretinal injection of PBS, AAV2.AcGFP, or AAV2.Flt23k. In each group, n = 5. The error bar represents the SD.