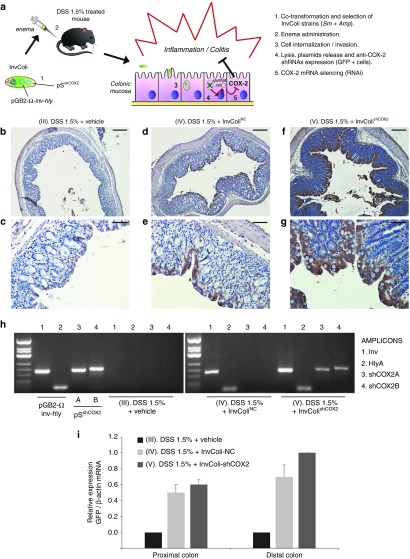
Figure 1.
InvColishCOX2 strategy is suitable for genetic material transfer in vivo. (a) E. coli (DH5α) is cotransformed with pGB2-Ω-inv-hly and pSshCOX2 plasmids to obtain the InvColishCOX2 strain, subsequently selected and administered via enema to colitic mice treated with DSS 1.5%. InvColishCOX2 bacteria penetrate colon epithelial cells and promote after endocytic lysis the expression of two short hairpin RNA (shRNA) targeting COX-2 mRNA. (b–g) GFP protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in FFPE colon specimens from experimental mice group III (DSS 1.5% + vehicle), IV (DSS 1.5% + InvColiNC), and V (DSS 1.5% + InvColishCOX2). Colon specimens were collected on day 7 (D7, start colitis, SC). (b,d,f) Scale bar = 200 µm; magnification ×50. (c,e,g) Scale bar = 50 µm; magnification ×200. Vehicle = LB medium. (h) PCR analysis of Inv-(1), HlyA-(2), shCOX2A-(3), and shCOX2B-(4) amplicons was performed on pGB2-Ω-inv-hly, pSshCOX2A/B purified plasmids and on total DNA extracted from group III, IV, and V (colon specimens). PCR products were analyzed after electrophoresis on 2.5% agarose gel. (i) GFP mRNA expression was analyzed by real-time PCR and normalized against β-actin mRNA levels. Relative expression was calculated referring to group V (distal colon, time D7) and data represent the mean + SEM of three independent analyses (n = 3 per group).