Fig. 2. Notch1 binding and activation by high-affinity DLL4 variants.
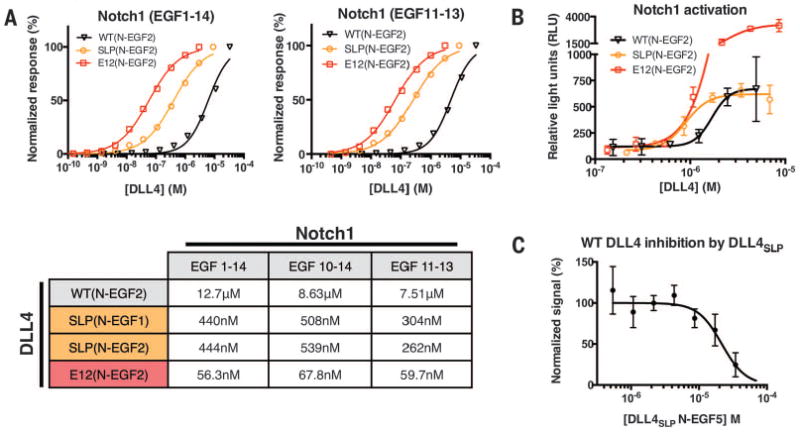
(A) Binding isotherms were obtained by surface plasmon resonance. Wild-type DLL4(N-EGF2), generation 1 DLL4SLP(N-EGF1 and N-EGF2) and generation 2 DLL4E12(N-EGF2) constructs were flowed over immobilized Notch1 EGF1–14, 10–14, or 11–13. Curves were fit to a 1:1 binding model to obtain the Kd values indicated in the table. (B) Notch1 activation was measured in a luciferase assay using cell lines expressing Notch1 and stably integrated with a luciferase gene under control of a CSL-driven promotor. Plates (96-well) were coated with serial dilutions of wild-type and high-affinity DLL4 variants. High-affinity mutants have increased potency relative to wild type. (C) Soluble DLL4SLP (N-EGF5) inhibited Notch1 activation by immobilized, wild-type DLL4(N-EGF5) in the luciferase assay.
