Figure 1. Nucleotide Exchange Factors and Hsp70.
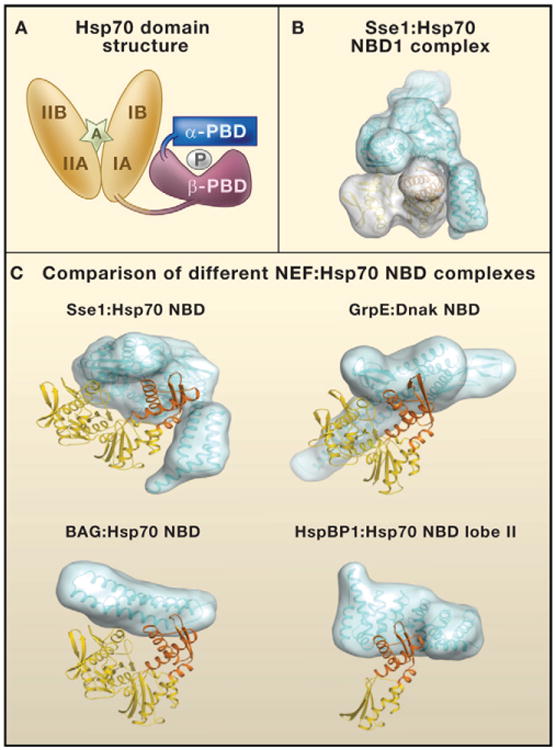
(A) The domain structure of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70). The nucleotide-binding domain (NBD; orange) consists of two structurally similar lobes (I and II) divided into four subdomains (IA, IB, IIA, and IIB). The peptide-binding domain (PBD) consists of two subdomains: PBD-α (blue) and PBD-β (purple). P denotes a polypeptide in the Hsp70 PBD. An adenosine nucleotide in the Hsp70 NBD is denoted by A.
(B) Surfaces on the Sse1 (blue):Hsp70 NBD (yellow) complex.
(C) Comparison of different complexes containing nucleotide exchange factors (NEFs; blue) and the Hsp70 NBD domain (yellow; NBD lobe II domain IIB in orange). NEFs are of the four unrelated eukaryotic NEF groups: Hsp110/Hsp170 family (Sse1), GrpE homolog (GrpE), Bcl-2-associated athanogene domain (BAG), and HspBP1 homolog (HspBP1). For Sse1:Hsp70 NBD, the domain with the three α-helical bundles in Sse1 that makes contact with lobe II is the α-PBD. DnaK is the Hsp70 of Escherichia coli. Models were calculated with data in the following PDB fles: 3d2f, 1 dkg, 1hx1, and 1xqs (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do).
