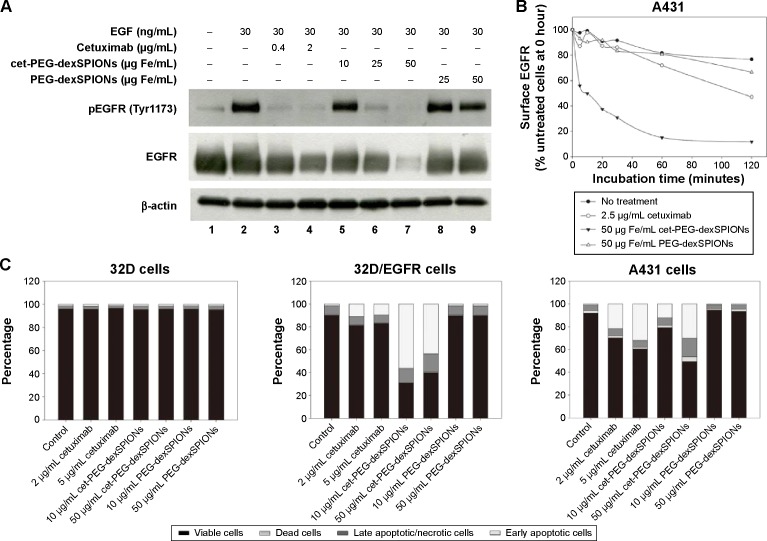
Figure 6.
Therapeutic effect of cet-PEG-SPIONs.
Notes: (A) Inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of EGFR by cet-PEG-dexSPIONs. A431 cells were serum-starved overnight and then treated with cetuximab, cet-PEG-dexSPIONs, or PEG-dexSPIONs at varying doses for 2 hours at 37°C. A431 cells were further stimulated with 30 ng/mL EGF for 30 minutes at 37°C. Cell lysates were separated by electrophoresis, and immunoblotting was performed to detect the p-EGFR (Tyr1173) and total EGFR levels. β-actin was used as a loading control. A representative of three blots is shown. (B) EGFR internalization in response to cet-PEG-dexSPIONs treatment in A431 cells. Cells were incubated for the indicated times in the presence of cetuximab (2.5 μg/mL), cet-PEG-dexSPIONs (50 μg Fe/mL), or PEG-dexSPIONs (50 μg Fe/mL). After stripping off the surface-bound cetuximab or nanoparticles, the cells were stained on ice for one hour with PE-conjugated mouse anti-human EGFR monoclonal antibody to determine the EGFR level remaining on the cell surface by flow cytometry. The expression level of EGFR on untreated A431 cells at 0 hours was set at 100%. (C) Apoptosis-inducing activity of cet-PEG-dexSPIONs in EGFR-expressing cell lines analyzed by an Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/propidium iodide assay. The stacked bar graph shows the proportion of different cell populations among the EGFR-null 32D cells, EGFR-overexpressing 32D/EGFR cells, and A431 cells.
Abbreviations: cet, cetuximab; dex, dextran; EGF, epidermal growth factor; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PE, phycoerythrin; SPIONs, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles; p-EGFR, phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor.