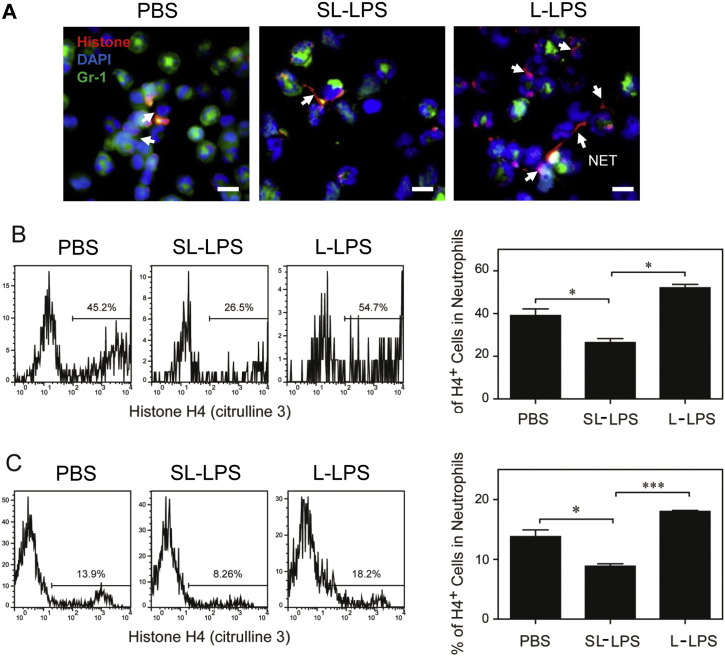
Fig. 4.
Differential regulation of NET formation by super-low and low dose LPS. (A) The PMN isolated from the peritoneal lavage 1 d after CLP from the mice pre-conditioned with either PBS, low dose LPS (L-LPS), or super low dose LPS (L-LPS) were spun on the slides. Neutrophils were stained with the anti-mouse Gr-1 antibody followed by biotinylated anti-Rat Ig antibody and Streptavidin-FITC (green). NETs were stained with the anti-citrullinated Histone H3 antibody followed by the biotinylated goat anti-rabbit Ig antibody and Streptavidin-PE (red). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). White arrow: NET. Scale bar = 30 μm. (B) C57 BL/6 mice were i.p. injected with super-low dose (5 ng/kg) or low dose (50 μg/kg) LPS. After 24 h, splenocytes were harvested and re-stimulated with PMA (50 nM) for 3 h. The levels of histone H4 (citrulline 3) within CD11b+/Ly6G+ neutrophils were analyzed by flow cytometry. The plotted data represent three independent experiments. (C) BM cells from C57 BL/6 mice were cultured with G-CSF (100 ng/mL) in the presence of either super-low dose (100 pg/mL) or low dose (1 μg/mL) LPS for 3 days, and fresh LPS was added to the cell cultures every 24 h. After stimulation with PMA (50 nM) for 3 h, the levels of histone H4 (citrulline 3) within CD11b+/Ly6G+ neutrophils were analyzed by flow cytometry. Quantitative data were shown as means ± SEM from three independently treated samples. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared between indicated groups (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001).