Figure 1.
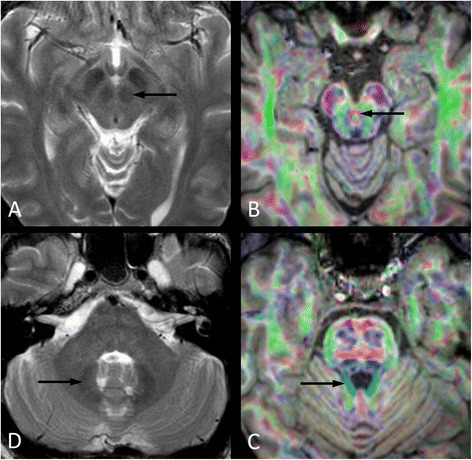
Most important anatomical structures involved in the cerebrocerebellar neurocognitive regulatory system; axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance images at the level of the midbrain (A) and brachium pontis (D) and cross-sectional color maps derived from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) with T1-weighted anatomical information at the level of the interpeduncular fossa (B) and the pons (C). The cerebellorubral tract connects the dentate nucleus (D, arrow) with the contralateral red nucleus (A, arrow). Its fibers are a component of the brachium conjunctivum (C, arrow) and cross the midline via the decussation (B, arrow) of the superior cerebellar peduncles (brachia conjunctiva) just below the level of the inferior colliculi.
