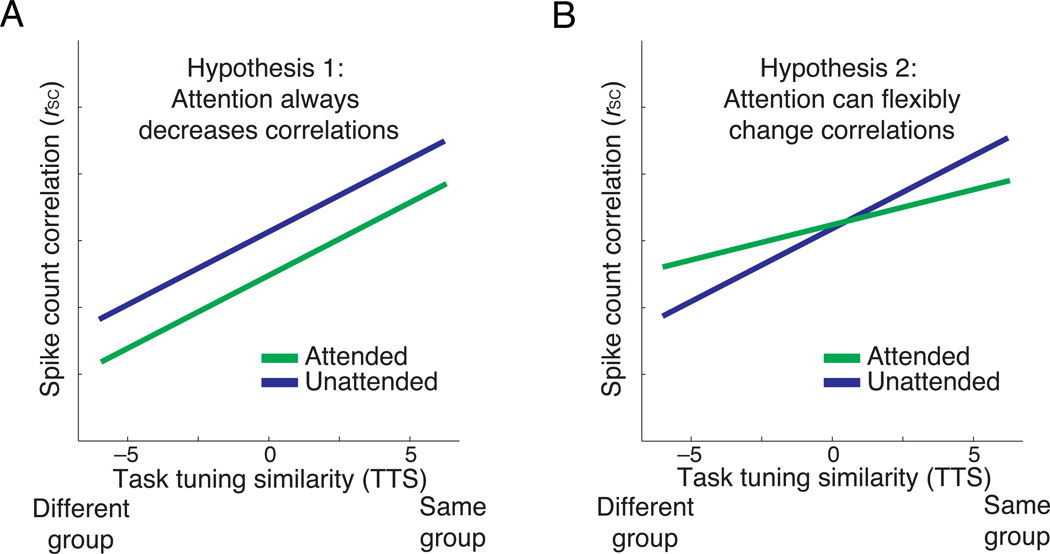
Figure 3. Hypotheses for how spike count correlations depend on TTS.
(a) Hypothesis 1: attention decreases correlations regardless of the relationship between a pair of unit’s tuning similarity. (b) Hypothesis 2: attention can either increase or decrease correlations. Under one model, if attention changes correlations to maximize information coding, correlations would be expected to decrease between pairs with positive TTS but increase between pairs with negative TTS.