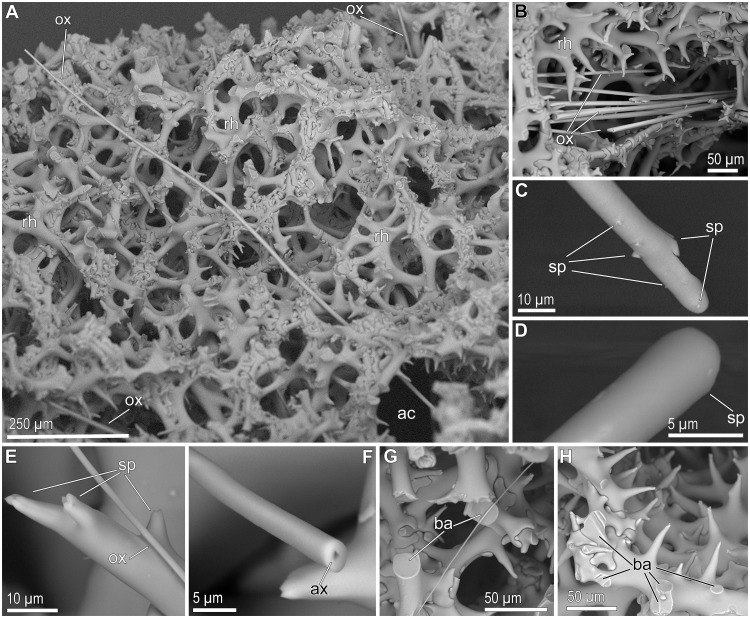
Fig 3. Skeletal details of Leiodermatium pfeifferae.
(A) General view of the desma (rh) network, with oxeas (ox) and aquiferous canals (ac) passing through. (B) Pack of oxeas (ox) running through the desma (rh) network. (C-D) Detail of the round, spiny (sp) ends of the thickest strongyloxeas occurring in the marginal fringe. (E) Detail of a very thin oxea (ox) on the typical multifurcated spine (sp) of a rhizoclon desma. (F) View of the triangular axial canal (ax) at the core of a broken oxea. (G-H) Broken arms (ba) of desma showing no internal axial canal.