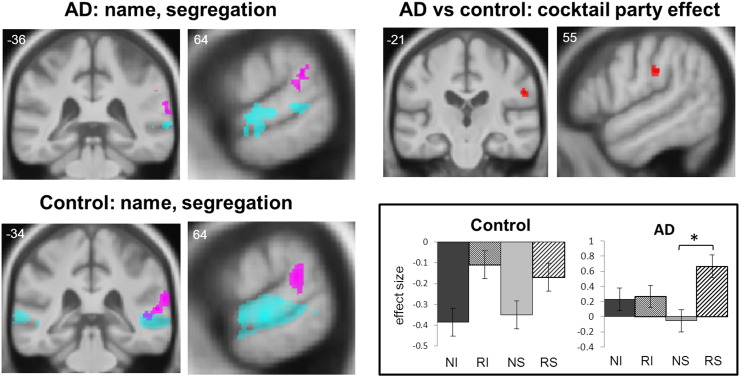
Fig. 2.
Statistical parametric maps (panels top row, bottom left) of regional brain activation for contrasts of interest in the Alzheimer's disease (AD) and healthy control groups and the between-group ‘cocktail party’ interaction; effect sizes (group mean ±1 standard error peak voxel beta parameter estimates) for each experimental condition at the right supramarginal gyrus peak from the cocktail party contrast are also shown (panel bottom right; * indicates significant difference in effect size between conditions, p < 0.01). Statistical parametric maps are rendered on coronal and sagittal sections of the study-specific group mean T1-weighted structural MR image in MNI space; the coordinate of each section plane is indicated and the right hemisphere is shown on the right in all coronal sections. Maps have been thresholded at p < 0.001 uncorrected over whole brain for display purposes; activations shown were significant at p < 0.05 after family-wise error correction for multiple comparisons over anatomical small volume of interest (see also Table 2). Contrasts were composed as follows: name identification (cyan), [(NS + NI) − (RS + RI)]; auditory object segregation processing (magenta), [(NI + RI) − (NS + RS)]; cocktail party effect (red), [(NI − RI) − (NS − RS)] where NI is own natural name interleaved with babble, NS own natural name superimposed on babble, RI spectrally rotated name interleaved with babble, RS spectrally rotated name superimposed on babble.