Figure 1.
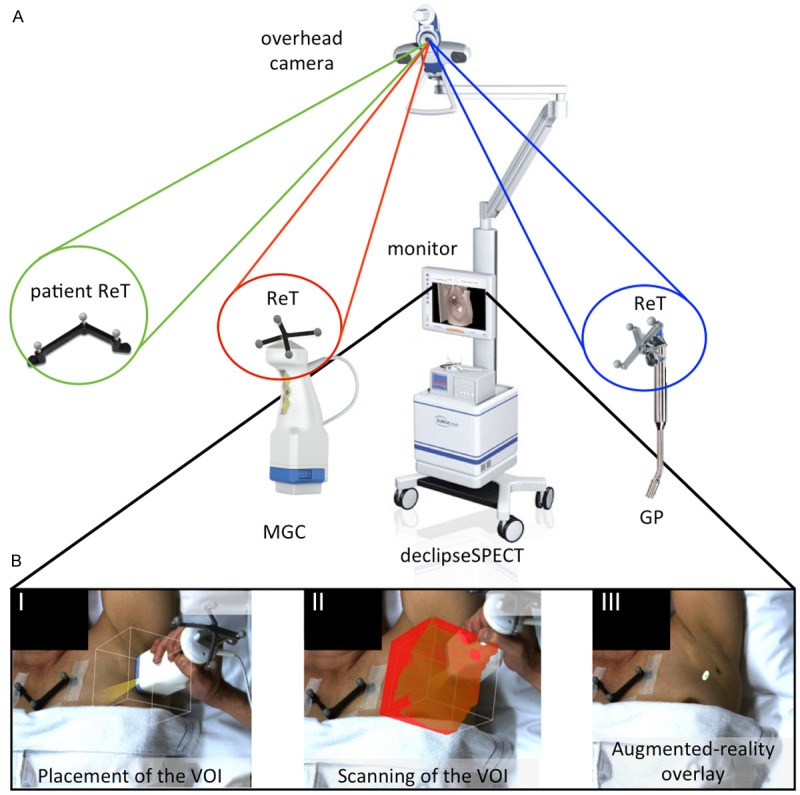
FreehandSPECT acquisition using the declipseSPECT-mobile gamma camera combination. A. Different components of the 3D-freehandSPECT-mobile gamma camera (3D-FHS-MGC) setup. A patient reference tracker (ReT) is placed on the patient. Additional ReTs are placed on the MGC and on the navigation tool (gamma probe (GP)). The position of the patient ReT as well as that of the MGC and the GP are optically tracked by the navigation system. An overhead camera records video-feed. This allows projection of the acquired 3D-FHS-MGC image on the patient thereby generating an augmented-reality image (part B of the figure). B. Generation of a 3D-FHS-MGC scan consists merely of three steps: I) Placement of the volume of interest (VOI) of the MGC over the sentinel node (SN) area; II) Scanning the VOI in three orthogonal directions; and III) Reconstruction of the acquired data results in the generation of a 3D-FHS-MGC augmented-reality image allowing the surgeon to navigate to the SN.
