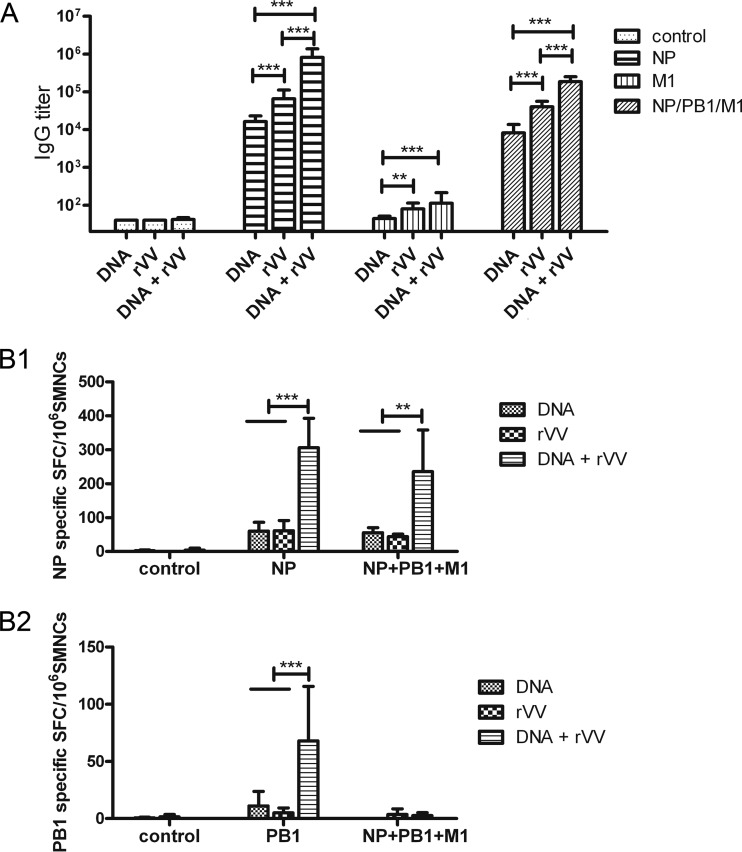
FIG 3.
Humoral and cellular immune responses induced by influenza virus PB1-, NP-, and M1-based vaccines. Mice were immunized intramuscularly with influenza virus PB1-, NP-, and M1-based DNA or rVV vaccines, according to the immunization schedule described in Table 1. (A) Humoral immune response in influenza virus PB1, NP, and M1 vaccine-immunized mice. A serum sample was obtained from each mouse at week 8, and the presence of IgG antibodies specific for influenza A virus was analyzed using ELISA. The bars show the geometric mean antibody titers, and the error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals (n = 14 mice/group). (B) Cellular immune responses in influenza virus PB1, NP, and M1 vaccine-immunized mice. Mice were sacrificed at week 8, and the spleens were separated under aseptic conditions and ground to isolate SMNCs (n = 3 mice/group). Next, 4 μg/ml NP147–155 (TYQRTRALV) (B1) and PB1317–325 (MFLAMITYI) (B2) were used as stimulants in ELISPOT assays. The numbers of SMNCs that produced IFN-γ after stimulation with peptides for 30 h are presented as spot-forming cells (SFCs)/106 SMNCs. The bars show mean SFCs/106 SMNCs, and the error bars indicate standard deviations. Lines above two or more groups indicate comparable results. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001 using one-way ANOVA.