Figure 7.
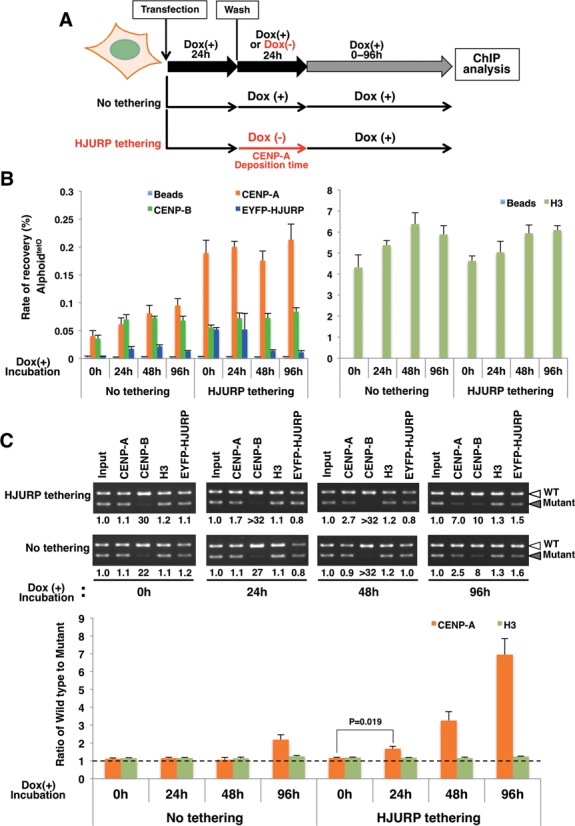
CENP-B binding to alphoid DNA enhances CENP-A retention on nucleosomes. (A) Schematic diagram of the CENP-A preassembly followed by the ChIP assay. After co-transfection with the wild type and mutant CENP-B box alphoidtetO DNAs, and a Halo-CENP-A expressing plasmid, the cells expressing tetR-EYFP-HJURP were cultured in medium containing doxycycline for 24 hr. To deposit the maximum level of CENP-A nucleosomes by the tethering of tetR-EYFP-HJURP at tetO sites on the transfected alphoidtetO DNAs, the cells were cultured with doxycycline-free medium for 24 hr. Then, doxycycline was added to the medium to quench the CENP-A deposition. The cells were harvested after 0, 24, 48 and 96 hr of culture in medium containing doxycycline. The ChIP assay and the quantitative PCR/competitive PCR were then performed. The black line indicates the culture with medium containing doxycycline. The red line indicates the culture with doxycycline-free medium, to deposit CENP-A. (B) The relative copy number of the total alphoidtetO array, quantitated by real-time PCR. The ChIP assay was performed with anti-CENP-A, anti-CENP-B, anti-histone H3, and anti-GFP (also recognizing EYFP) antibodies. The bars show the relative rates of recovery of the total alphoidtetO DNA against the input DNA. Error bars represent the SEM (n = 3). (C) DNA samples recovered after the ChIP assay were analyzed by competitive PCR. The relative enrichment of the wild type CENP-B box alphoidtetO DNA versus the mutant CENP-B box alphoidtetO DNA is shown below the gel images. White arrowheads indicate the PCR fragments from the wild type CENP-B box alphoidtetO DNA. Gray arrowheads indicate the PCR fragments from the mutant CENP-B box alphoidtetO DNA. The values of CENP-A and H3 are normalized by the input DNA. Error bars represent the SEM (n = 3). P-values obtained with the t-test are indicated.
