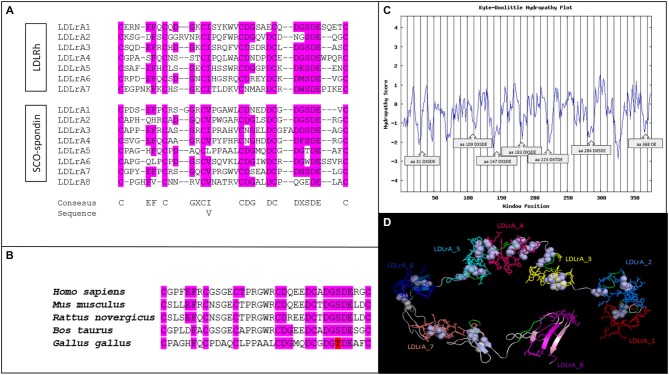
Figure 1.
Bioinformatics analyses of LDLrA domains present in the SCO-spondin sequence of Gallus gallus. (A) Multiple alignment of SCO-spondin LDLrA domains and comparison with the LDLrA domain sequence of the human LDL receptor (LDLRh). (B) Multiple alignment of the SCO-spondin LDLrA5 domain from different species. For all species analyzed this domain conserved the DxSDE motif, or a conservative substitution of serine to threonine (in red). (C) Hydropathic plot of the SCO-spondin sequence that contains the LDLrA domains, showing its hydrophilic character, especially for the regions containing the DxSDE motifs. (D) Tertiary structure of the SCO-spondin region that contains the LDLrA domains arranged in tandem. Each domain is shown in a different color; DxSDE motifs are highlighted in green, and disulfide bridges are in white.