Fig. 1.
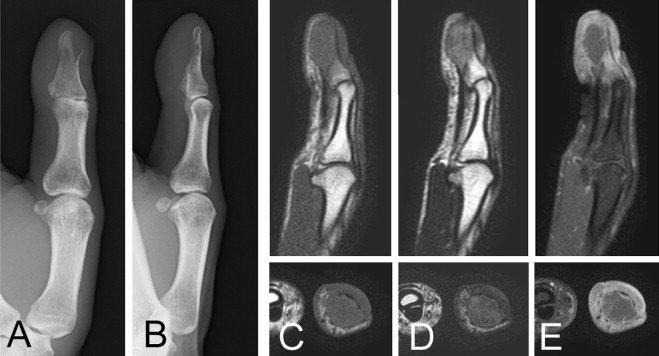
Plain radiographs show that the cortical bone of the distal phalanx has disappeared at the flexor side, and the remaining bone is thinned (A and B). MRI images display low signal intensity on T1-weighted images (C), and heterogeneous low to moderate signal intensity on T2-weighted images (D). No gadolinium enhancement is observed inside of the lesion (E).
