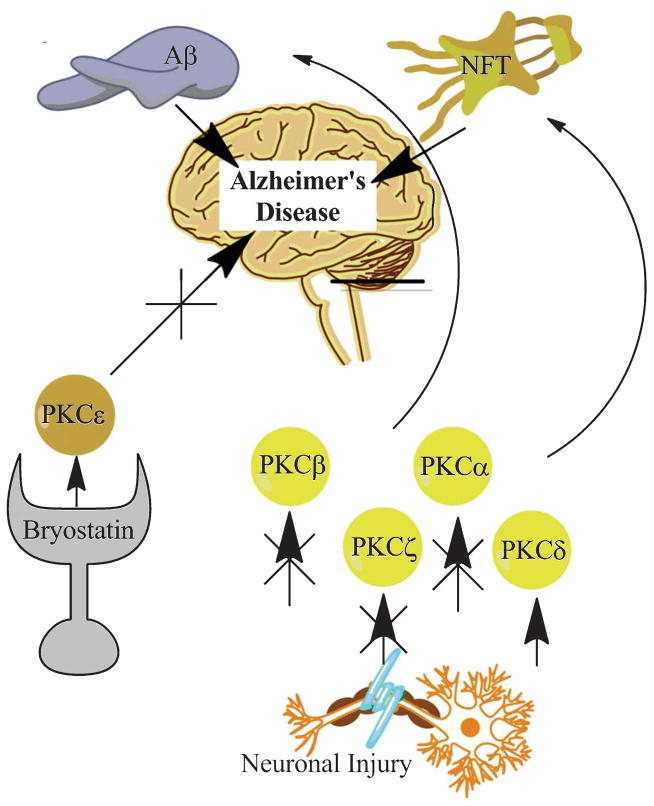
Fig. 2.
Neuronal injury causes dysregulation of PKC β, ζ, and α as well as an increase in PKCδ. These changes contribute to the development and progression of Aβ pathology and NFTs. Targeting PKCε with the pharmacologic agent Bryostatin may prove beneficial in protecting the brain against harmful PKC changes. By increasing PKCε, the progression of NFTs and Aβ pathology will be slowed.