Figure 2.
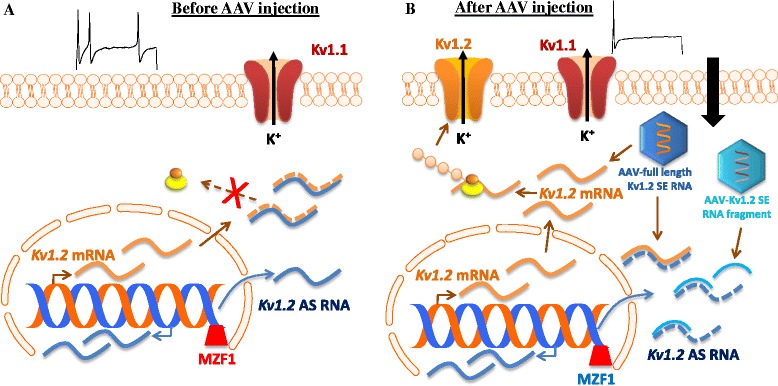
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) mediated transfer of Kv1.2 sense RNA for the reduction of DRG neuronal excitability. (A) Before AAV injection into the DRG of rats with peripheral nerve injury, a nerve injury-induced increase in DRG Kv1.2 AS RNA triggered by MZF1 knocks down expression of Kv1.2 mRNA and protein, resulting in an increase in DRG neuronal excitability under neuropathic pain conditions. (B) After AAV injection into the DRG of rats with peripheral nerve injury, AAV mediated transfer of full length Kv1.2 sense (SE) RNA rescues nerve injury-induced DRG Kv1.2 downregulation at the DRG neuronal membrane through not only its direct translation into Kv1.2 protein but also its indirect blockage of nerve injury-induced increase in Kv1.2 AS RNA expression via extensive overlap of their complementary regions. AAV mediated transfer of Kv1.2 SE RNA fragment (-311 to +40) also rescues nerve injury-induced DRG Kv1.2 downregulation through its blockage of nerve injury-induced increase in Kv1.2 AS RNA expression via partial overlap of their complementary regions, although this RNA fragment cannot be translated into Kv1.2 protein. Maintaining normal Kv1.2 expression at DRG neuronal membrane reduces nerve injury-induced neuronal hyperexcitability at DRG neurons and consequently decreases spinal central sensitization, resulting in neuropathic relief.
