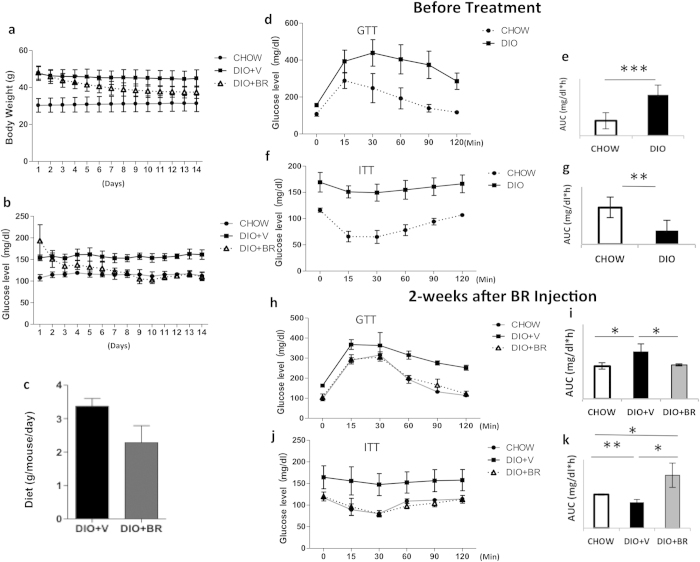
Figure 1. Administration of bilirubin reduces body weight and increases insulin sensitivity in DIO mice.
(a) Changes in body weights of DIO mice treated with bilirubin (DIO + BR) or vehicle (DIO + V) compared to control mice fed standard diet (CHOW). (b) Daily non-fasting blood glucose levels in DIO + BR, DIO + V, and CHOW mice during bilirubin treatment. (c) Average food intake per mouse per 24-h period in DIO mice receiving BR or vehicle. (d) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (GTT) of DIO mice and CHOW controls before bilirubin treatment; (e) area under the curve of GTT. (f) Insulin tolerance test (ITT) of DIO mice and CHOW mice before bilirubin treatment; (g) reverse area under the baseline above curve. (h) GTT of DIO + BR, DIO + V, and CHOW mice 14 days after the first bilirubin injection; (i) area under the curve. (j) ITT of DIO + BR, DIO + V, and CHOW mice at 14 days after the first bilirubin injection; (k) reverse area under the baseline above curve. At least 6-8 mice were included in each group; **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, Student’s t test. DIO + BR: DIO mice treated with bilirubin; DIO + V: DIO mice treated with vehicle; CHOW: mice fed standard diet.