Figure 1.
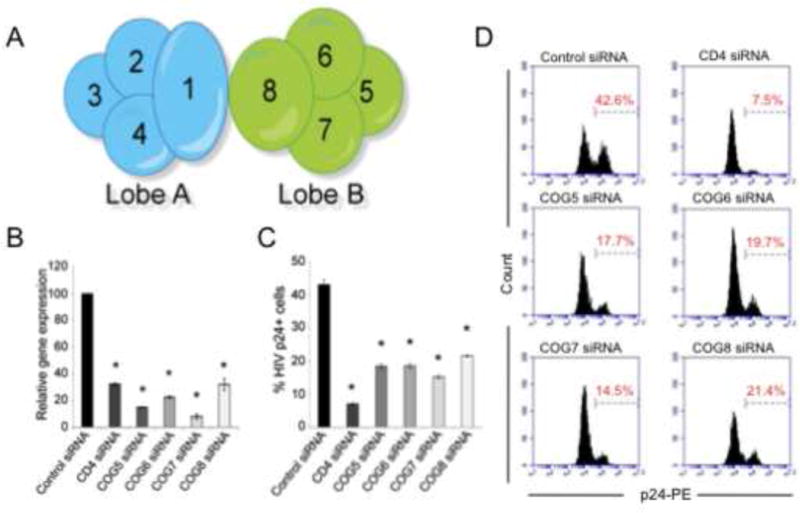
RNAi-mediated silencing of components of the COG complex, COG5, -6, -7 or -8 impairs HIV-1 replication. (A) Schematic representation of the components of the COG complex that are divided into two lobes (lobe A and B) linked through interactions with COGs 1 and 8. (B) P4R5 MAJI cells were transduced with siRNAs targeting COG5, -6, -7, or -8, CD4 or a non-specific control sequence (control siRNA). The silencing of the cognate target genes was measured by quantitative real time PCR (N=3, *p<0.002, two-tailed t-test) relative to expression levels in the control siRNA treated cells. All values were normalized to GAPDH expression. (B and C) The silencing of COG5, -6, -7 or -8 significantly inhibited HIV-1 gag expression compared to the control siRNA-treated cells. The siRNA treated cells were infected with HIV-1 IIIB and the intracellular level of HIV-1 gag (p24) was measured 48 hours later. Shown are the averaged inhibition of p24 expression (±Standard deviation (S.D.)) normalized to the Control siRNA treated cells (C) (N=3, *p<0.002, two-tailed t-test) and representative histograms (D).
