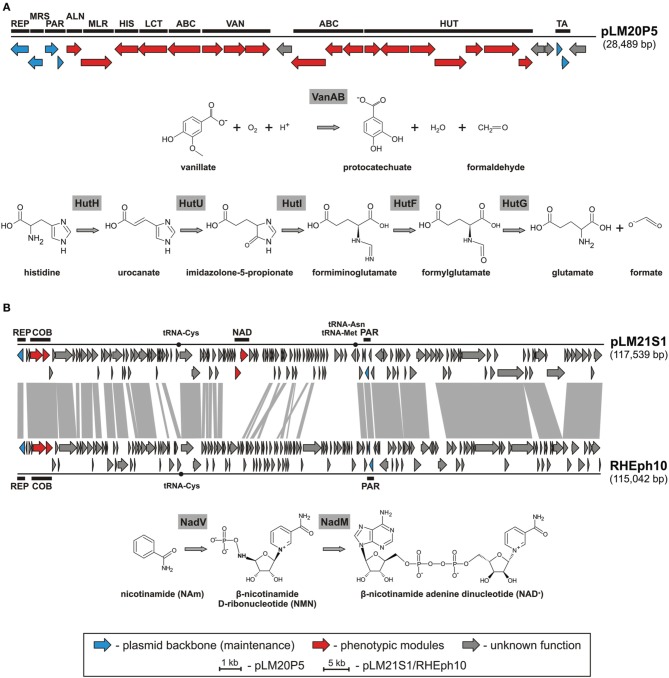
Figure 3.
Linear map showing the genetic structure of the circular plasmid pLM20P5 of P. yeei LM20 and schematic pathways for vanillate and histidine utilization (A), and linear map showing the genetic structures of the circular plasmid-like prophage pLM21S1 of Sinorhizobium sp. LM21 and Rhizobium phage RHEph10, and a schematic pathway for NAD biosynthesis (B). The predicted genetic modules are indicated by black rectangles: ABC, ABC-type transporter system; ALN, allantoate amidohydrolase; COB, part of a cobalamine biosynthesis module; HIS, histidinol-phosphate aminotransferase; HUT, histidine utilization system; LCT, D-lactate dehydrogenase; MLR, microcystin LR degradation protein; MRS, multimer resolution system; NAD, NAD+ biosynthesis module; PAR, partitioning system; REP, replication system; TA, toxin-antitoxin system; VAN, vanillate utilization system. Arrows indicate genes and their transcriptional orientation. The tRNA-encoding sequences are marked by black dots. The gray-shaded area connects genes of plasmid pLM21S1 and phage RHEph10 that encode homologous proteins.