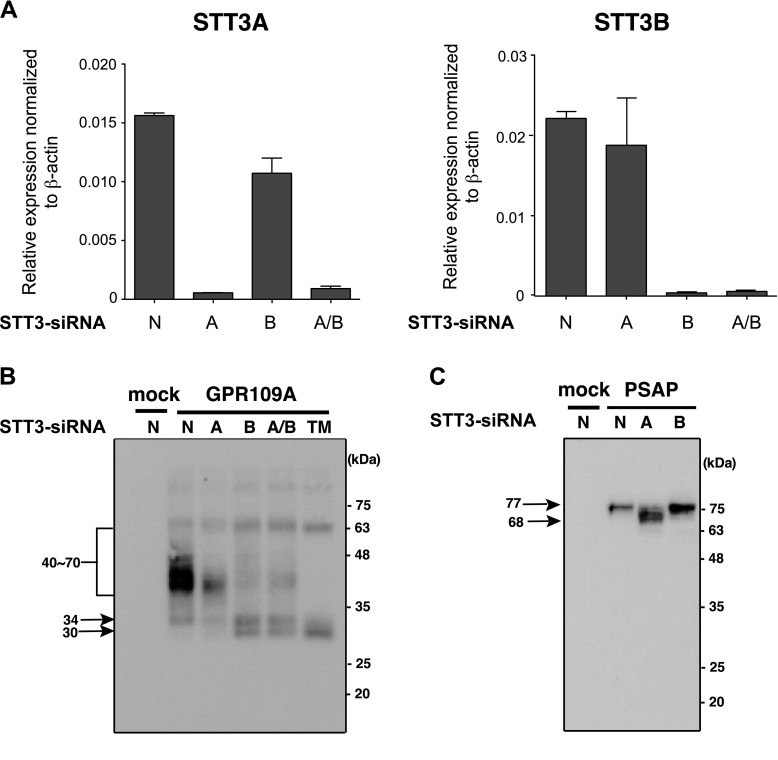
Figure 4.
STT3B is required for efficient hGPR109A N-glycosylation. A) Endogenously expressed STT3A and STT3B mRNAs were knocked down in HeLa cells by using 50 nM isoform-specific STT3 siRNAs (STT3A-siRNA, STT3B-siRNA, or mixture of STT3A and STT3B-siRNAs). Relative STT3A and STT3B mRNA expression levels were determined using real-time reverse transcriptase PCR analysis. Values were normalized to β-actin mRNA levels. B, C) HeLa cells were cultured for 24 hours prior to transfection with 50 nM siRNA (STT3A-siRNA, STT3B-siRNA, mixture of STT3A and STT3B-siRNAs, or nontargeting siRNA). Forty-eight hours after siRNA transfection, the cells were transfected with hGPR109A/WT and hPSAP plasmids, and were harvested 16 hours later. The molecular masses of hGPR109A and hPSAP were determined using SDS-PAGE and Western blot analyses, as described in the Materials and Methods. A, STT3A-siRNA; B, STT3B-siRNA; A/B, mixture of STT3A and STT3B-siRNAs; N, nontargeting siRNA; TM: tunicamycin-treated.