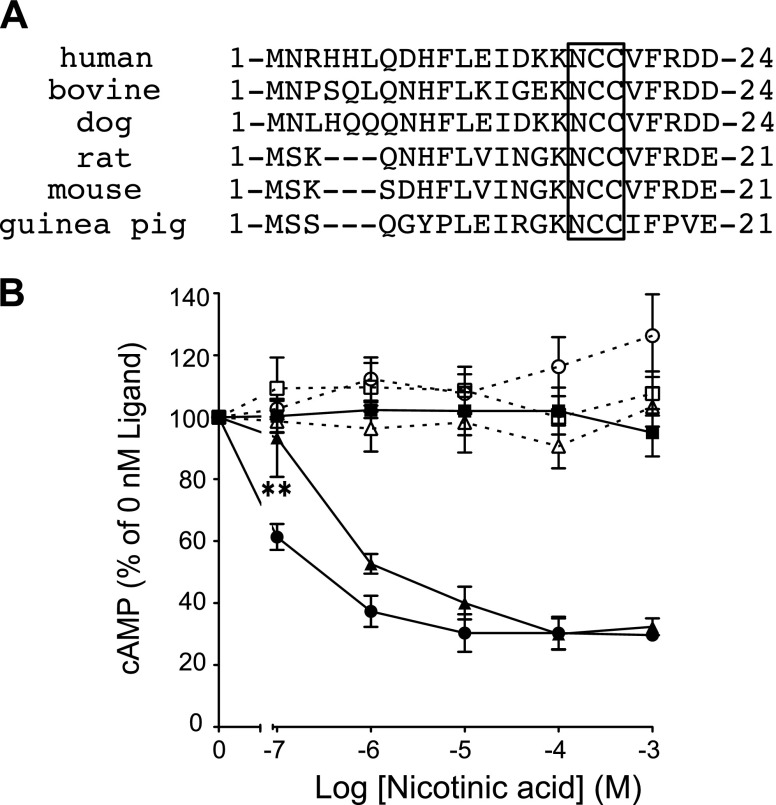
Figure 5.
hGPR109A N-glycosylation contributes to nicotinic acid-induced intracellular signaling. A) Amino acid sequences of mammalian GPR109As were obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database (human ID: EU012026, bovine predicted sequence ID: XM002694482, dog predicted sequence ID: XM543378, rat ID: NM181476, mouse ID: NM030701, guinea pig ID: EF185820). N-terminal Asn-Cys-Cys sequences in each GPR109A are boxed. B) Stimulatory effects of nicotinic acid on forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation in CHO-K1 cells transiently expressing hGPR109A/WT (full circles) or hGPR109A/N17A (full triangles), or in empty vector-transfected cells (mock, full squares). These cells, hGPR109A/WT (open circles), hGPR109A/N17A (open triangles), and mock (open squares) cells, were pretreated with 100 ng/ml PTX for 6 h. Data are represented as the mean ± se (n = 3). Statistical analysis was carried out for hGPR109A/N17A (nontreated, full triangles). Data are representative of 3 independent experiments that yielded similar results. **P < 0.01 vs. hGPR109A/WT; ANOVA with Tukey post hoc pairwise comparisons.