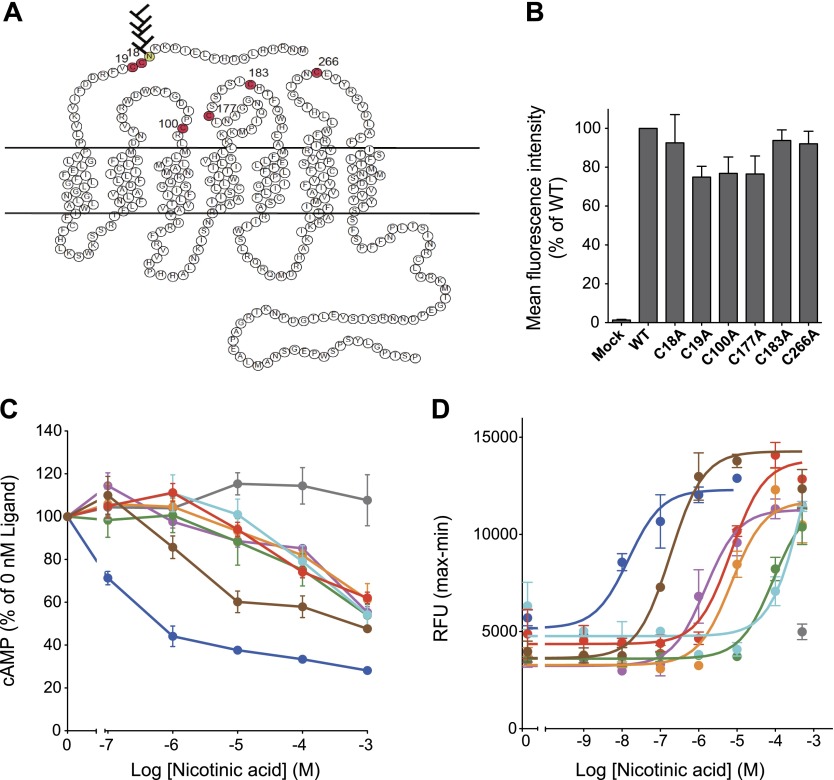
Figure 7.
Extracellular cysteine residues in hGPR109A are important for nicotinic acid-induced intracellular signaling. A) Secondary structure of hGPR109A. Extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic regions are based on the structure of rhodopsin. Amino acid symbols in red indicate cysteine residues in the extracellular regions of hGPR109A. B) Twenty-four hours after transfection with mock, hGPR109A/WT, /C18A, /C19A, /C100A, /C177A, /C183A, or /C266A plasmids, surface expression levels in CHO-K1 cells were determined using flow cytometric analysis. C) Stimulatory effects of nicotinic acid on forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation in CHO-K1 cells transiently expressing hGPR109A/WT (blue), /C18A (purple), /C19A (orange), /C100A (green), /C177A (aqua), /C183A (red), /C266A (brown), or those transfected with empty vector (mock, gray). D) Stimulatory effects of nicotinic acid on the intracellular [Ca2+] levels in CHO-K1 cells stably expressing hGPR109A/WT (blue), /C18A (purple), /C19A (orange), /C100A (green), /C177A (aqua), /C183A (red), or /C266A (brown), or those transfected with empty vector (mock, gray). Data are represented as means ± se (n = 3) and are representative of 3 independent experiments that yielded similar results. Average EC50 values for hGPR109A/WT, /C18A, /C19A, /C100A, /C177A, /C183A, and /C266A in 3 independent experiments were 7.9 nM (WT), 1.8 μM (C18A), 7.4 μM (C19A), 77.4 μM (C100A), 300 μM (C177A), 9.5 μM (C183A), and 541 nM (C266A).