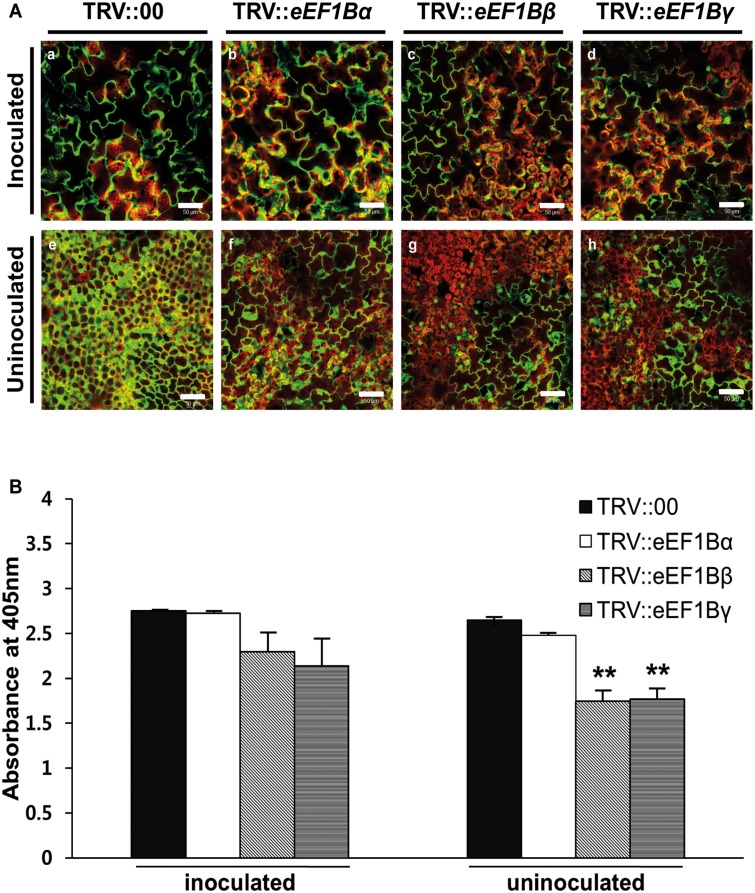
Fig 3. Effects of eEF1Bα-, β- or γ-silencing on PVX infection in N. benthamiana.
(A) Spreading of PVX-GFP in eEF1B subunit-silenced plants and TRV::00 control plants. Fluorescence was visualized at 7 dpi in the inoculated (a-d) and uninoculated leaves (e-h). Green fluorescence signal indicates presence of GFP-fused PVX and chloroplasts are revealed by red autofluorescence. Scale bars = 50 μm. (B) Accumulation levels of PVX in gene-specific silenced plants. Accumulation of PVX in the inoculated and uninoculated leaves was tested by DAS-ELISA 5 days after PVX infection. This time point corresponds to 18 days after TRV agroinfiltration. Nine plants were tested in 3 independent repeats, with 3 biological plants for each treatment. The error bars indicate standard error. Asterisks denote significant differences between TRV::00 and eEF1B-silenced plants (unpaired t-test: **P <0.01).