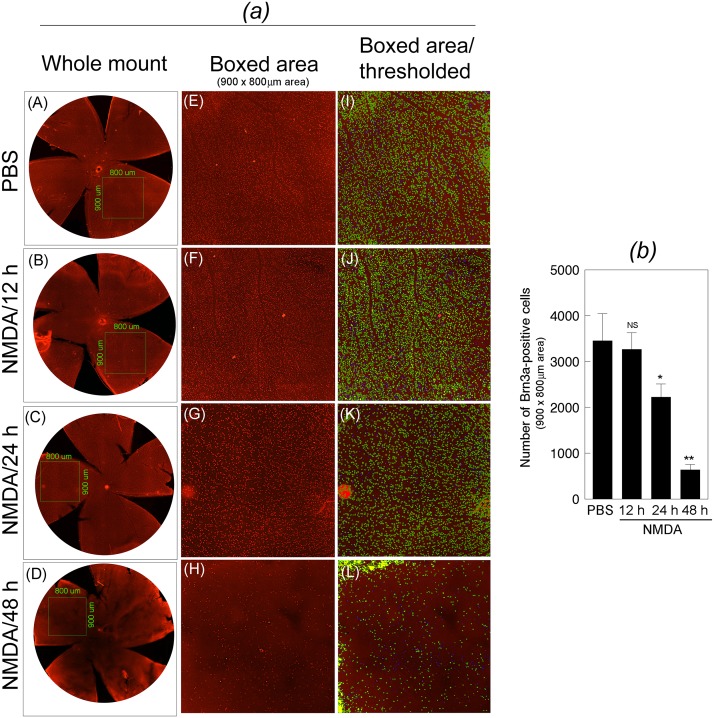
Fig 4. Characterization of RGCs’ loss in the retina.
(a) After treating the eyes with PBS (panel A) or NMDA, whole retinas were isolated at 12 h (panel B), 24 h (panel C), and 48 h (panel D), and immunostained with antibody against Brn3a. From each retina, the number of Brn3a-positive RGCs in the boxed areas (four areas per retina) of equal size (900 x 800 um size; panels E, F, G, and H) were quantified by adjusting the threshold of the images (panels I, J, K, and L) and by using Nikon elements AR software. Results presented in the figure indicate that when compared to the Brn3a-positive RGCs in the retinas isolated from PBS-treated eyes (panels A, E, I), the number of Brn3a-positive RGCs in the retinas isolated at 12 h (panels B, F, J), 24 h (panels C, G, K), and 48 h (panels D, H, L) after NMDA-treated eyes was decreased progressively over time. (b) Quantification of the Brn3a-positive cells indicate that when compared to PBS treatment, NMDA treatment significantly decreased the number of RGCs,. *, **p<0.05. NS, not significant.