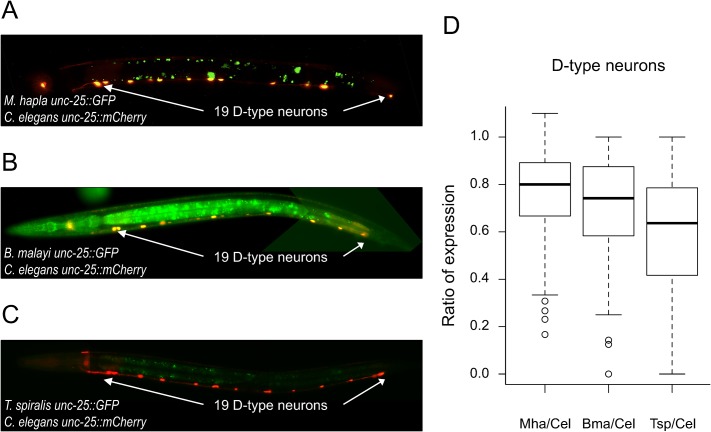
Fig 3. unc-25 regulatory sequences from distantly-related nematodes drive expression in C. elegans.
(A-C) C. elegans unc-25 regulatory sequence drives expression of mCherry in all transgenic strains; (A) M. hapla, (B) B. malayi, (C) T. spiralis unc-25 regulatory sequences drive expression of GFP. Animals were photographed at 400x magnification. Images are false-colored composites of single animals. Separate GFP and mCherry images are shown in S2 Fig. (D) Ratios of the number of D-type neurons expressing GFP/mCherry in individuals carrying each transgene pair (see Materials and Methods and S1 Table for total counts). While each strain drives expression in D-type neurons, the three strains do show differences in their distributions of the ratios of cells expressing GFP relative to mCherry (Kruskal-Wallis test, p = 1.53×10−5).