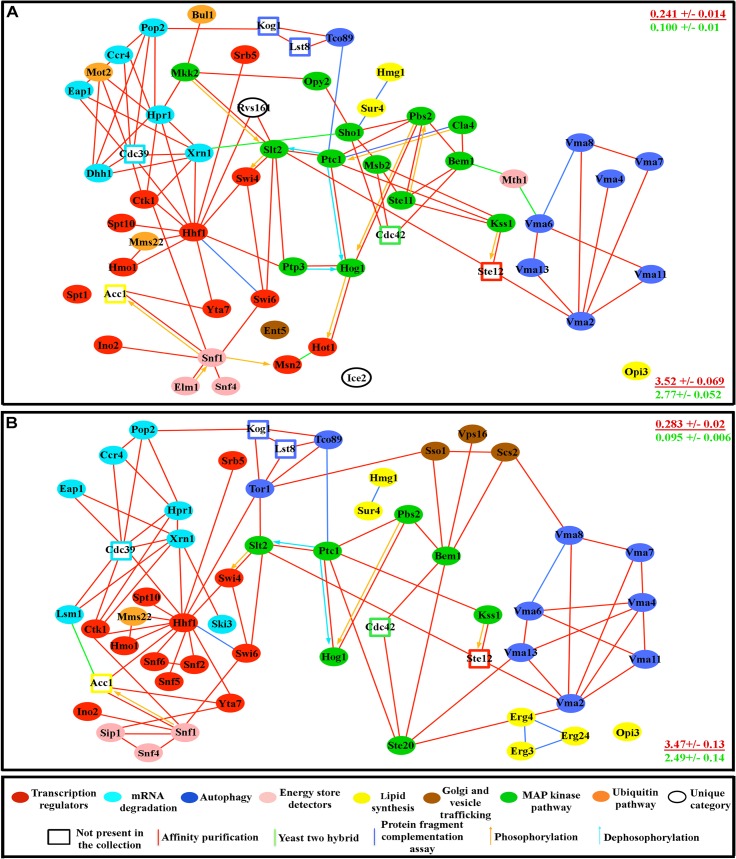
Fig 5. Genes for which mutations affect conversion of glucose or aspartic acid to fat affect connected proteins.
(A) Proteins encoded by genes for which mutation produces more than a 20% increase in the rate of conversion of 14C labeled D-glucose to fat relative to wild-type tend to be proteomically connected to one another. (B) Proteins encoded by genes for which mutation produces more than a 20% increase in the rate of conversion of 14C labeled L-aspartic acid to fat relative to wild-type tend to be proteomically connected to one another. At the right side of each panel is the global clustering coefficient (upper) and path length (lower) for each subnetwork (red font), presented over the mean of values from 10,000 simulated random networks with the same degree distribution and vertex count as the subnetwork in that panel (green font). Key for diagrams as in Fig 1.