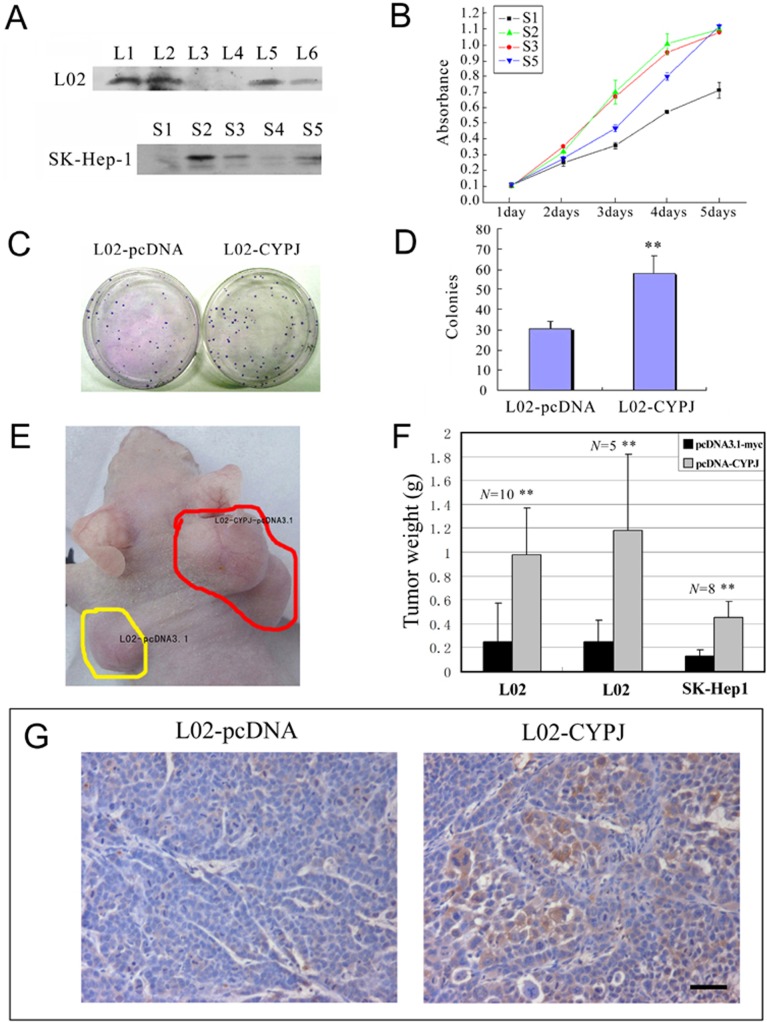
Fig 6. Overexpression of CYPJ promoted the growth of human cell line SK-Hep1 and L02.
(A) Cell clones with CYPJ protein by stable cell transfection were identified by western blot using anti-myc monoclonal antibodies. L3, L4 and S1 are negative control cells stably transfected with empty vector pcDNA3.1-myc. (B) Growth curves of the recombinant cells with or without exogenous CYPJ were obtained from MTS assays. Each sample was tested in triplicate and the error bars are included. (C) and (D), promotion of colony formation by CYPJ in normal liver cell line L02. (C) Expression of CYPJ promoted the colony formation in L02 cells. L02 cells were transfected with either pcDNA3.1-myc vector (left) or with CYPJ-expression vector (right). (D) Percentage of G418 resistant colonies. Data were results of 3 independent experiments. ** P<0.01. (E), (F) and (G), CYPJ promoted in vivo tumorigenicity of L02 and SK-Hep1 cells. (E) Recombinant cells with or without exogenous CYPJ were injected into each side of nude mice, respectively, and tumor weight was measured. (F) Compared with control tumors, tumors originated from cells with overexpressed CYPJ were significantly heavier. ** P<0.01. (G) Immunohistochemical staining using anti-myc monoclonal antibody indicated the expression of exogenous CYPJ. Scale bar indicated 50 μm.