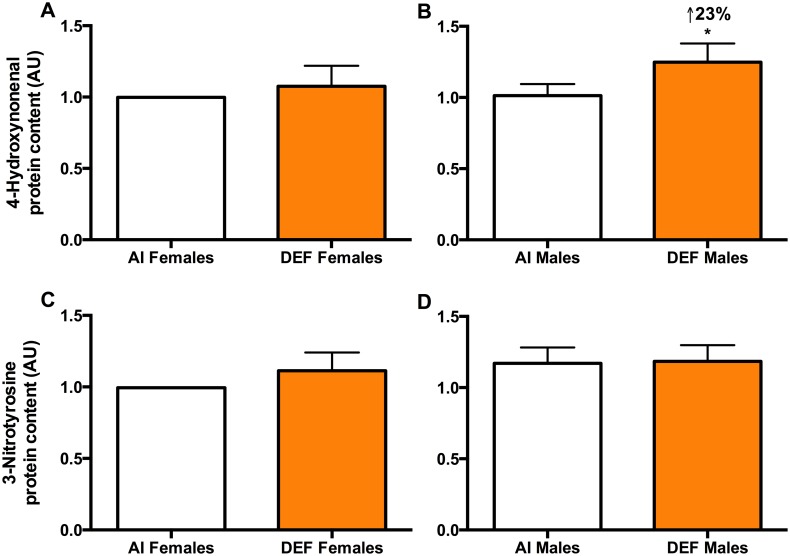
Fig 1. Oxidative damage in DEF vs. AI G93A mice.
4-HNE (A and B) and 3-NY (C and D) protein content (arbitrary units; AU) in spinal cord of 42 G93A mice: 23 adequate vitamin D3 intake (AI; 1 IU D3/g feed; 12 M, 11 F) and 19 deficient vitamin D3 intake (DEF; 0.025 IU D3/g feed; 10 M, 9 F). 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE, A and B): DEF mice had 16% higher 4-HNE protein content vs. AI (P = 0.056). DEF males had 23% higher 4-HNE protein content vs. AI males (P = 0.066). 3-Nitrotyrosine (3-NY, C and D): There was no significant difference in 3-NY protein content between the diets. AI males had 18% higher 3-NY protein content vs. AI females (P = 0.073). Data presented as means ± SEM.