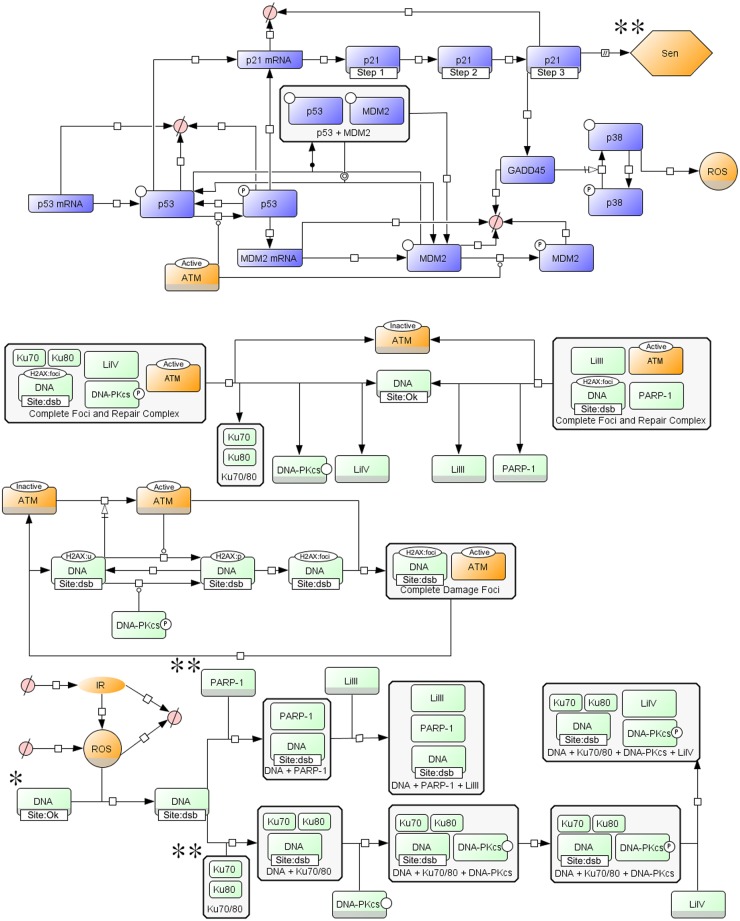
Fig 1. Integrated model of DNA damage repair by non-homologous end joining and p53/p21 mediated early senescence signalling.
A basic graphical model in SBGN process diagram format [58], with NHEJ in green [16], p53/p21-mediated early senescence signalling in blue [4] and parts of the model that have been recalibrated or added in orange. In the NHEJ part of the model, DNA double stranded breaks are induced and then repaired by either D-NHEJ or B-NHEJ. In the signalling part, activated ATM triggers phosphorylation of the p53/p21 and activation of pathways that lead to senescence. The DNA entities (marked by *) represent 50 separate DNA species that undergo damage and repair independently. After the cells reaches an early senescent state (Sen) the abundance of Parp-1 and Ku70/80 slowly decreases (**) (see S2 Table for details). The presented NHEJ part is a reduced version of the full NHEJ part with two types of double-stranded breaks (simple and complex) (see S1 Text for detailed description of the model). A gray bar at the bottom of a molecular species indicates that the same species is presented several times in the model; in other words the same molecule can participate in many different reactions. A full description of SBGN, and a key for the components in an SBGN compliant process diagram can be found at http://www.sbgn.org/