Fig 3. PAR1 or PAR4 activation reduces urothelial MIF in mouse bladder.
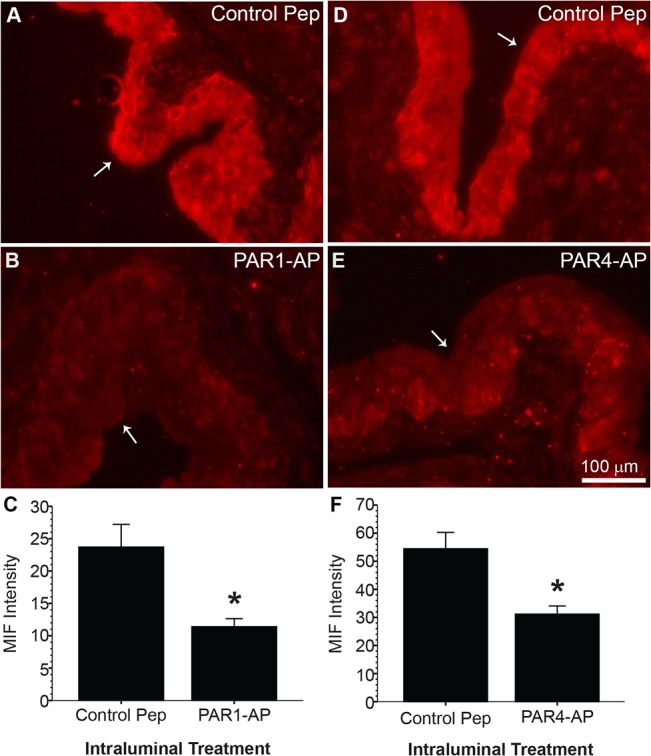
Female mice under anesthesia, received intravesical instillation of a PAR1 or PAR4 activating peptide (AP) or a respective scrambled peptide (Control Pep: RLLFT-NH2 for PAR1; YAPGKF-NH2 for PAR4) for one hour before harvesting bladders. Panels (A, B, D, E) show MIF immunofluorescent labeling in representative bladders. White arrows point to intraluminal surface of the urothelia. MIF immunofluorescent labeling localized to urothelium (A, D) and a decrease in urothelial MIF immunofluorescence was observed after PAR1-AP (B) or PAR-4-AP (E) treatment when compared to control peptide-treated groups (A, D). Densitometry showed that average urothelial MIF immunofluorescence (N = 6 per group) significantly decreased after intravesical PAR1- (C) or PAR4-AP (F) treatment when compared to respective control groups (* p ≤ 0.05).
