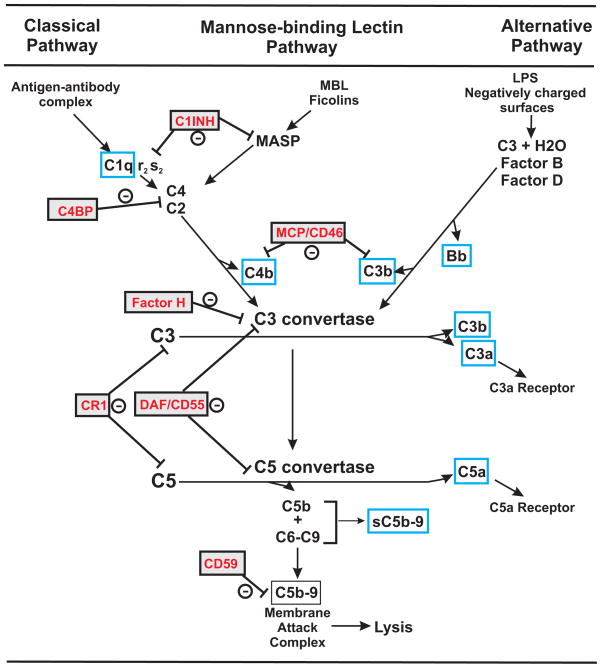
Figure 1. Complement System.
Three activation pathways of complement are depicted with regulators of complement activation in red text. Blue boxes highlight products of complement activation of interest in normal pregnancy or associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes. The C3 convertase is a molecular complex generated from the classical or lectin pathway (C4bC2a) and the alternative pathway (C3bBb) that cleaves C3 generating the C5 convertase (C4bC2aC3b or C3bBbC3b). Once activated, C3b and C4b can be further degraded to smaller fragments C3d and C4d that are still covalently bound to target and maintain many biological activities but do not participate as components of the C3 and C5 convertase to propagate activation of the pathway. The rodent specific regulator of complement activation Crry (CR-1 related gene y) is not included but has CD46/CD55 like activities. C1-INH, C1 inhibitor; MCP, membrane cofactor protein; C4BP, C4 binding protein; CR1, complement receptor 1; DAF, decay accelerating factor; MASP, mannose associated serine protease; MBL, mannose binding lectin