Figure 2.
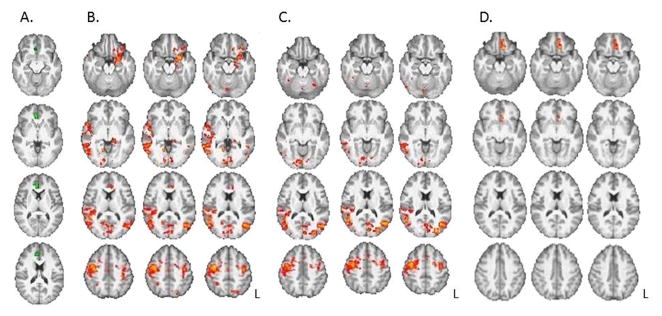
Relationships between resting-state connectivity strength of the rostral anterior cingulate cortex and Precontemplation scores (B, C) and years of regular methamphetamine use (D).
A. Rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) seed (in green). B. Connectivity maps show negative relationships between Precontemplation scores and connectivity strength between rACC and amygdala, parahippocampal gyrus, medial and lateral orbital frontal cortex, bilateral precentral gyrus, temporal lobe, bilateral occipital cortex and cerebellum. C. After covarying for years of regular methamphetamine use, relationships between Precontemplation and connectivity of the rACC were attenuated, with remaining relationships in precentral cortex, occipital cortex and right middle frontal gyrus. D. The relationship between connectivity strength of the rACC with years of methamphetamine use, independent of Precontemplation. All results controlled for age, gender, inpatient status and years of education (p’s < 0.016, whole-brain cluster corrected). L = left hemisphere.
