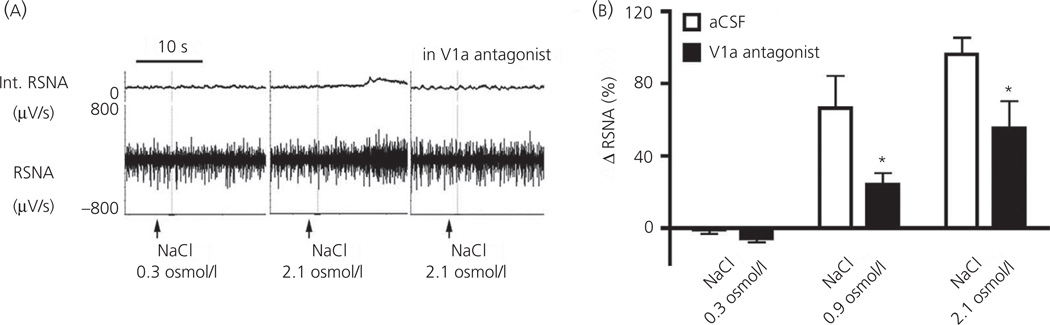
Fig. 5.
Dendritically-released vasopressin (VP) contributes to osmotieally-driven renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA). (a) Recordings or RSNA after intracar-otid infusions of an isosmotic (NaCl 0.3 osmol/l) or hyperosmotic (NaCl 2.1 osmol/l) solution, in the absence or presence of bilateral microinjections of the V1a receptor antagonist (0.4 mg/ml) into the paraventricular nucleus (PVN). (b) Summary data showing a dose-dependent increase of RSNA after intracarotid infusions of NaCI. Note the blunted sympathetic response after an intra-PVN microinjection of the V1a receptor antagonist [*P < 0.0001 versus respective artificial cerobrospinal fluid (aCSF)]. Modified from Brussaard et al. (56).