Figure 6.
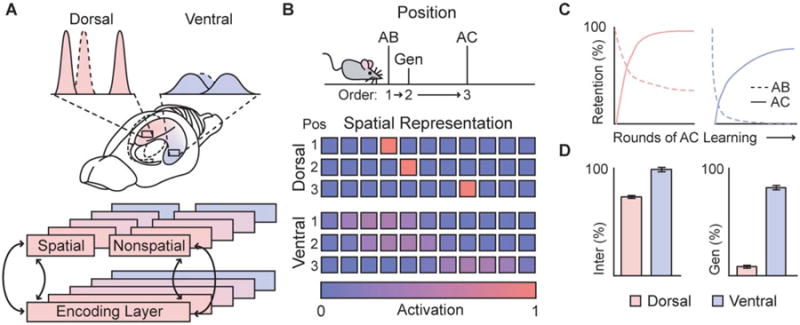
Modeling of the mnemonic impact of a spatial representational gradient. A, B) Diagrams of model details. A) Each hippocampal population was modeled with an identical autoassociator. DH and VH simulations only differed in the sparseness of their spatial representations, with no differences in their nonspatial input. B) An AB/AC paradigm was used to test the influence of sparse and distributed spatial representations on interference and generalization of nonspatial associates. AB and AC lists were learned at different locations, corresponding to different spatial representations. C) Learning and forgetting curves for both lists during the course of AC list learning. AB associations were learned above 95% performance level before AC list learning. D) Magnitude of interference and generalization effects in both populations. nter: interference, Gen: generalization. Histogram bars represent mean plus one standard error of the mean.
