Figure 4.
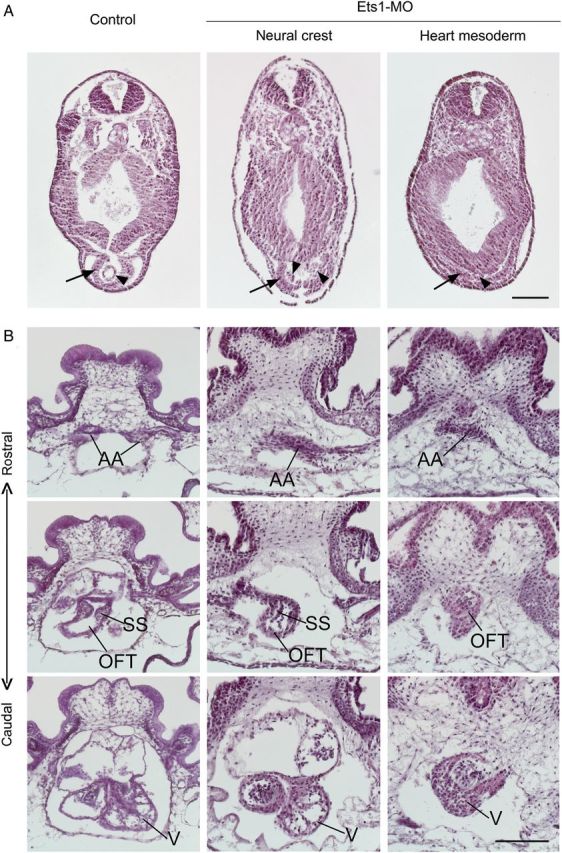
Ets1 is required in both cardiac NC and heart mesoderm for heart formation. Embryos receiving Ets1-MO in NC cells or heart mesoderm on both sides were collected at stage 28 (A) for examining primitive heart tube formation or stage 45 (B) for chambered heart formation. The embryos were transversely sectioned and stained with haematoxylin–eosin for better visualization of their histology. (A) In control embryo, a single endothelial heart tube forms inside a partially closed myocardial heart tube (n = 3). Ets1-MO in NC does not affect such heart tube formation despite a slight delay in the fusion of the endocardial tube (n = 2). In contrast, Ets1-MO expression in heart mesoderm abolishes the formation of the primitive heart tube (n = 4). The layer of cardiac myocytes is present but fails to form a tube. Arrows indicate myocardium and arrowheads indicate endocardium. (B) At stage 45, three-chambered heart is formed. From rostral to caudal sections, paired aortic arch arteries (AA) join at the OFT, which then connects with a single ventricle (V). Spiral septum (SS) shows as partial ridges in the section. Two atria are also visible dorsal to the ventricle. When Ets1 is knocked down in NC, the formation of aortic arch arteries is disrupted (n = 4). The vessels of the artery are not distinct, and often missing on one side. The OFT is also somewhat misshapen, although the spiral septum is still present. Most caudally, the ventricle and atria are largely unaffected. When Ets1-MO is expressed in heart mesoderm, the formation of the heart is essentially destroyed (n = 3). The heart is basically a single chamber with thick myocardium, continues from OFT to ventricle, with blood trapping inside. All sections are arranged with dorsal to the top. Scale bar = 0.2 mm.
