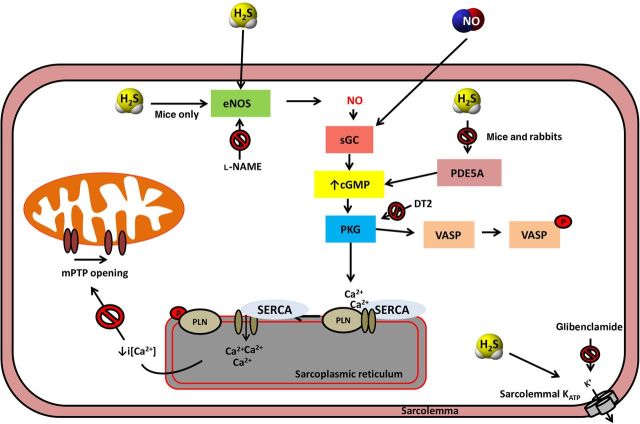
Figure 6.
Proposed molecular pathways of H2S-induced cardioprotection. Administration of H2S activates endothelial NOS resulting in NO release that in turn stimulates guanyl cyclase. H2S can also inhibit PDE. Both pathways (eNOS activation and PDE inhibition) operate in the mouse, whereas only PDE inhibition occurs in rabbits.