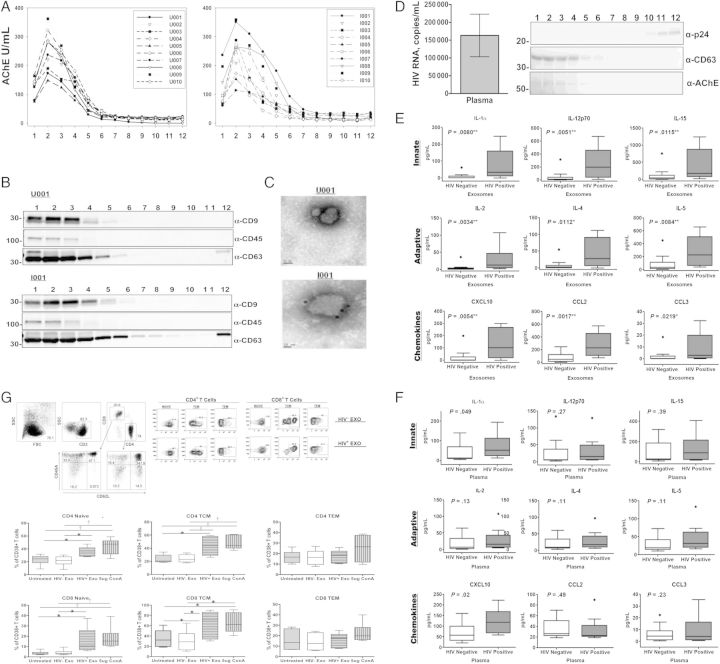
Figure 1.
Exosomes are efficiently purified from human plasma, analyzed for cytokine content, and examined for immunomodulatory potential. Plasma collected from whole blood in ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tubes was subjected to differential centrifugation at 30 000 g for 30 minutes and 100 000 g for 2 hours. The 100 000 g pellet was resuspended in 1 mL of ×1 phosphate-buffered saline, loaded onto Optiprep velocity gradients, and subjected to flotation centrifugation at 250 000 g for 2 hours. A–C, Fractions from individuals seropositive (n = 10) or seronegative (n = 10) for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) were subjected to an enzymatic assay for acetylcholinesterase (AChE), a marker for exosomes (A) and Western blot analysis for exosomal markers CD9, CD45, and CD63 (B) and were immunolabeled with anti-CD63 and examined with electron microscopy to confirm preparation of purified exosomes (C). D, Plasma viral loads of HIV-infected volunteers ranged from 1423 to 536 436 HIV-1 RNA copies/mL, with an average viral load of 205 957 HIV RNA copies/mL. Representative fractions from an HIV-1–seropositive individual were assayed for exosomal markers and HIV-1 viral particles via Western blot analysis to confirm purification of exosomes from HIV-1 viral particles. Purified exosomes and whole plasma from individuals seropositive (n = 10) or seronegative (n = 15) for HIV-1 were analyzed for proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression using a 21-plex multiplex array. E, All 21 proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines measured (interleukin 1α [IL-1α], interleukin 2 [IL-2], interleukin 2Rα [IL-2Rα], interleukin 4 [IL-4], interleukin 5 [IL-5], interleukin 7 [IL-7], interleukin 9 [IL-9], interleukin 12p70 [IL-12p70], interleukin 15 [IL-15], interleukin 16 [IL-16], CD40L, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), interferon [IFN] β and α2, CXCL10, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, soluble Fas ligand [sFasL], soluble intracellular adhesion molecule 1 [sICAM], and tumor necrosis factor [TNF] α) were associated with and significantly elevated in the exosomes of HIV-1–seropositive individuals compared with seronegative controls (a selection of representative cytokines comparing HIV-1–seropositive and seronegative controls is displayed). F, Alternatively, IL-1α, IFN-α2, and CXCL10 were significantly elevated in the corresponding plasma of HIV-1–seropositive individuals compared with seronegative controls. Error bars represent mean and standard error of the mean (SEM) from independent donors. Difference between groups were tested for statistical significance with the Mann–Whitney U test. *P < .05; †P < .01; ‡P < .001. G, CD38 expression was increased on the surface of naive and central memory CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells. A total of 3.0 × 106 peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 6 HIV-1–seronegative individuals were exposed to either pool exosomes isolated from the plasma of 3 HIV-1–seropositive (HIV+ Exo) or HIV-1–seronegative (HIV− Exo) individuals, left untreated, or treated with 5 µg/mL of concanavalin A (ConA) as a positive control. 48 hours after exposure, Naive (CD45RA+/CD62L+), central (TCM; CD45RA−/CD62L+) and effector (TEM; CD45RA−/CD62L−) memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were analyzed for CD38 expression using flow cytometry. Exosomes were normalized by total protein and added at a concentration of 1 μg/mL. Error bars represent mean and SEM values from 6 independent donors. Differences between groups were tested for statistical significance with 1-way analysis of variance. *P < .05; †P < .01; ‡P < .001.