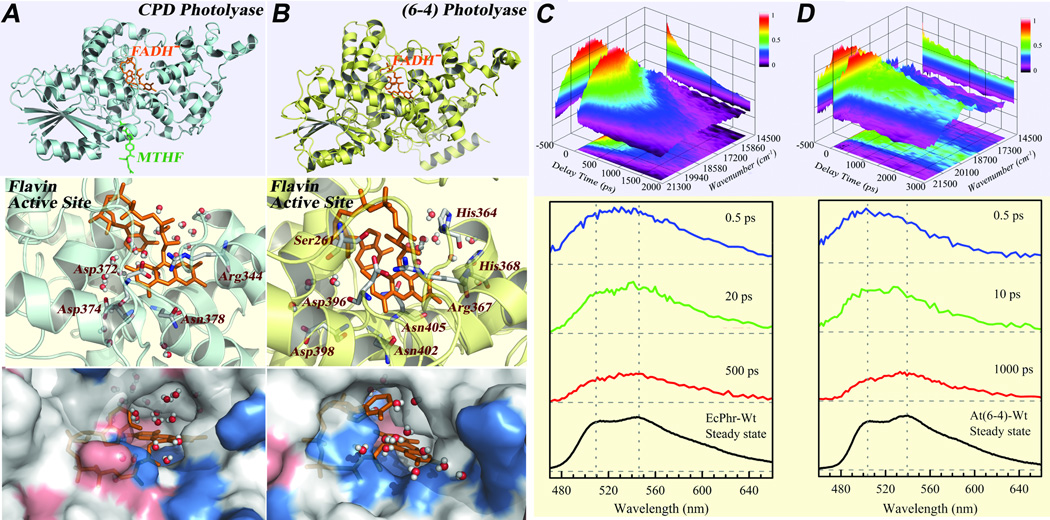
Fig. 4.
Active-site structures of photolyases and solvation dynamics probed by intrinsic flavin cofactor FADH−.31 (A-B) Top panel: X-ray structures of E. coli CPD photolyase and A. thaliana (6–4) photolyase with the catalytic cofactor (FADH−) in the center. Middle panel: Close-up view of the flavin and the active site of CPD photolyase (Left) and of (6–4) photolyase (Right) with the neighboring polar/charged residues and trapped-water molecules within 8 Å from one snapshot of 1-ns MD simulations. Bottom panel: Corresponding surface maps of the MD snapshots, showing the local topography, chemical property (red, negative charged residue; blue, positive charged residue), and trapped-water molecules at these active sites. (C-D) Upper panel: 3D representation of fs-resolved emission spectra of EcCPD (C) and At(6–4) (D) relative to time (ps) and emission energy (cm−1). The intensity was scaled by a color code. Lower panel: Snapshots of fs-resolved spectra at three typical delay times for the two sites with their corresponding steady-state emission spectra. For comparison and clarity, the steady-state emission peaks were marked by the gray dotted lines as references to show spectral peak and shape evolution.