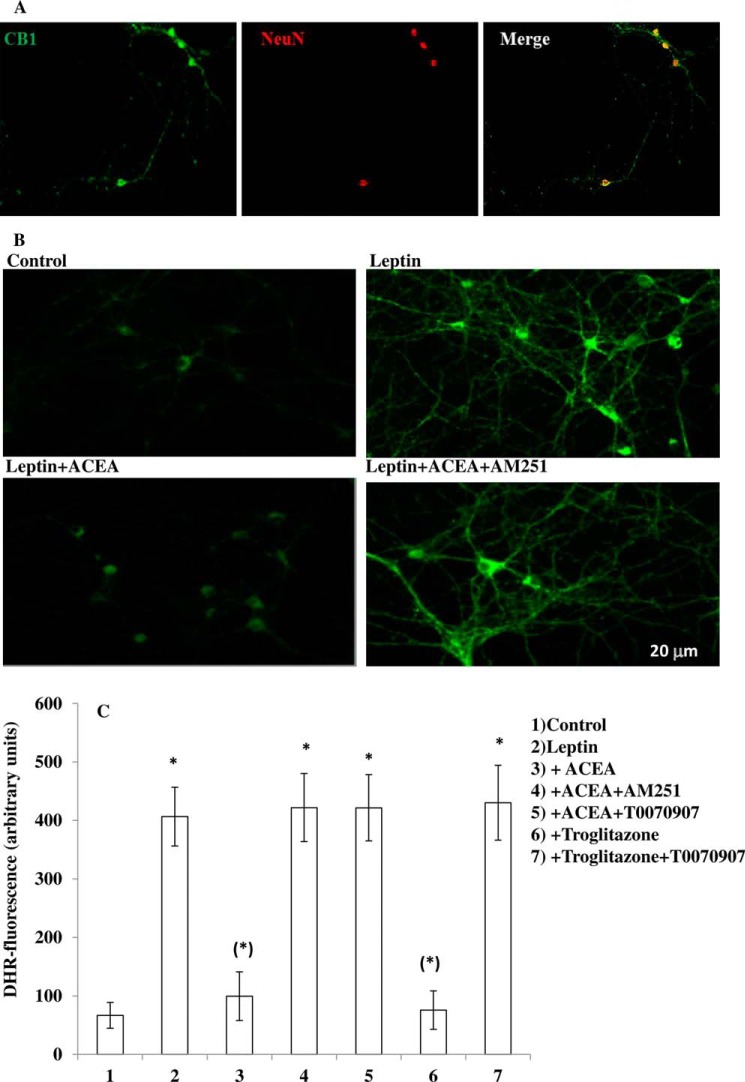
FIGURE 3.
A CB1 as well as a PPAR-γ agonist decrease leptin-induced ROS levels in primary cultures of hypothalamic ARC neurons. A, immunocytochemical staining of the CB1 (green signal) receptor in primary culture of hypothalamic neurons. Neuronal-specific nuclear protein (NeuN) antibody (red signal) was used as marker of neuronal cells. B, representative micrographs of ROS accumulation in primary culture of hypothalamic ARC neurons exposed to 100 ng/ml leptin for 4.5 h after a 30-min preincubation with DMSO or 0.5 μm ACEA with or without 0.5 μm AM251. A representative micrograph of control cells is also shown. C, DHR-loaded cells were incubated with AM251 (0.5 μm) or T0070907 (1 μm). After 30 min, cells were exposed to ACEA (0.5 μm) or troglitazone (1 μm) for an additional 30 min and, finally, treated with leptin (100 ng/ml; 4.5 h). After the treatments, the cells were analyzed with a fluorescence microscope as described in Fig. 1A. Results represent the mean ± S.E. of three separate experiments, each performed in duplicate. *, p< 0.01 compared with untreated cells; (*), p < 0.01 compared with leptin-treated cells (one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's test).