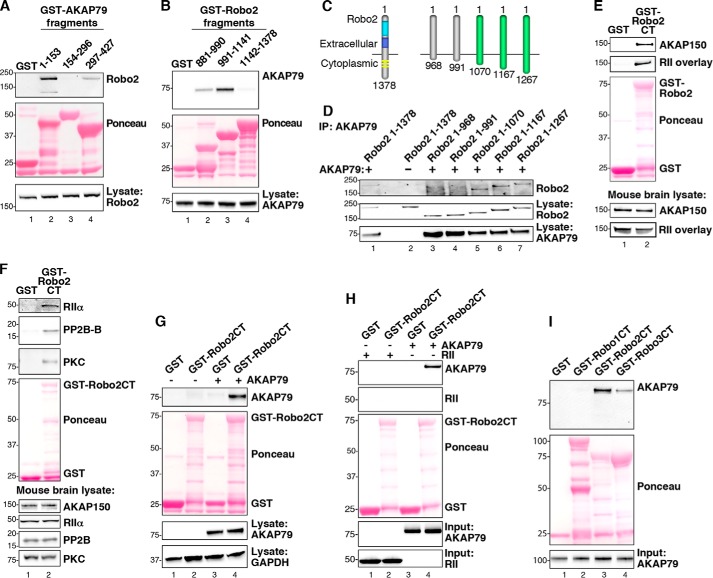
FIGURE 2.
Biochemical characterization of the Robo2-AKAP79/150 interaction. A, purified GST-AKAP79 fragments containing GST alone (lane 1) and amino acids 1–153 (lane 2), 154–296 (lane 3), and 297–427 (lane 4) were used to isolate Robo2 from HEK293 cell lysates. Molecular weight markers are indicated. B, GST-tagged fragments, including GST alone (lane 1) and amino acids 881–990 of Robo2 (lane 2), 991–1141 of Robo2 (lane 3), and 1142–1378 of Robo2 (lane 4), were used to pull down overexpressed AKAP79 from HEK293 cell lysates. C, diagram depicting progressive truncation of the Robo2 receptor used for fine mapping of the AKAP79 binding site. The first and last residues of each fragment are denoted. D, AKAP79 and truncated Robo2 receptors were overexpressed in HEK293 cells. AKAP79 immune complexes were immunoprecipitated (IP), and Robo2 binding was assessed by immunoblot. E, purified Robo2 C terminus (Robo2-CT) fused to GST was incubated with mouse brain lysate. Immunoblots were probed for AKAP150 (top) and overlaid with digoxigenin-labeled RII (top middle). F, GST-Robo2CT pull-downs from mouse brain lysate were immunoblotted for RIIα (top), PP2B (second from top), and PKC (third from top). G, GST-Robo2CT pull-downs from HEK293 cell lysate containing overexpressed AKAP79 were probed for AKAP79 (top). H, GST-Robo2CT was incubated with either purified His-AKAP79 or His-RII. GST-Robo2CT complexes were immunoblotted for AKAP79 (top) and RII (top middle). I, the C termini of Robo1, Robo2, and Robo3 were each fused to GST and purified from bacteria. Purified His-AKAP79 was incubated with the GST-RoboCT proteins, and immunoblots of the GST-Robo complexes were probed for AKAP79 (top).