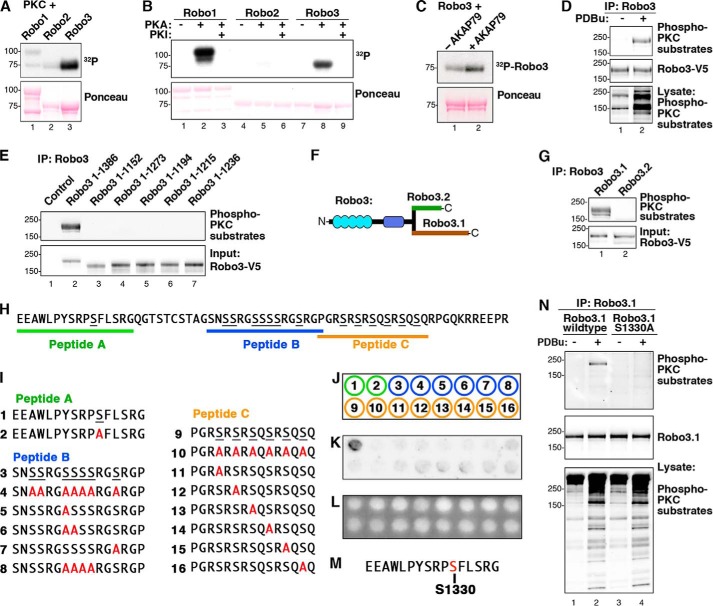
FIGURE 5.
PKC phosphorylates Ser-1330 in the cytoplasmic tail of Robo3.1. A, GST-Robo1CT, -Robo2CT, and -Robo3CT were phosphorylated by PKC in vitro. 32P incorporation was assessed by autoradiography. B, GST-Robo1CT, -Robo2CT, and -Robo3CT were phosphorylated using PKA in vitro, and 32P incorporation was assessed by autoradiography. C, GST-Robo3CT was phosphorylated by PKC in vitro plus or minus purified AKAP79. D, Robo3 was overexpressed in HEK293 cells. Cells were stimulated with vehicle (DMSO) or 2 μm PDBu for 10 min. Robo3-V5 immunoprecipitations (IP) were probed using an antibody that recognizes phosphorylated consensus (phospho-Ser) PKC phosphorylation sites (top). E, Robo3 receptors containing progressive C-terminal truncations were expressed in HEK293 cells and stimulated with PDBu. V5 immunoprecipitations were immunoblotted with the phospho-PKC substrate antibody. F, diagram depicting the differing distal C termini of Robo3.1 and Robo3.2. G, Robo3.1 and Robo3.2 were expressed in HEK293 cells. Cells were treated with PDBu, and V5 immunoprecipitations of cell lysates were immunoblotted with the PKC substrate antibody (top). H, unique Robo3.1 C-terminal amino acid sequence. Three Robo3.1 peptides containing putative PKC phosphorylation sites are indicated. I, peptides containing putative PKC sites from Robo3.1 and serine to alanine-substituted peptides. J, peptides 1–16 in I were synthesized using peptide spot array according to template. K, peptide array membrane was in vitro phosphorylated with PKC and [32P]ATP. The autoradiograph shows phosphorylated peptide. L, UV illumination of membrane shown in K validates equal spotting efficiency for all peptides. M, sequence surrounding the Ser-1330 phosphosite from peptide A. N, HEK293 cells expressing full-length wild type or S1330A Robo3.1 were treated with vehicle alone (DMSO) or PDBu. Robo3.1 immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted using the phospho-PKC substrate antibody to show phosphorylation of Robo3.1.