FIGURE 6.
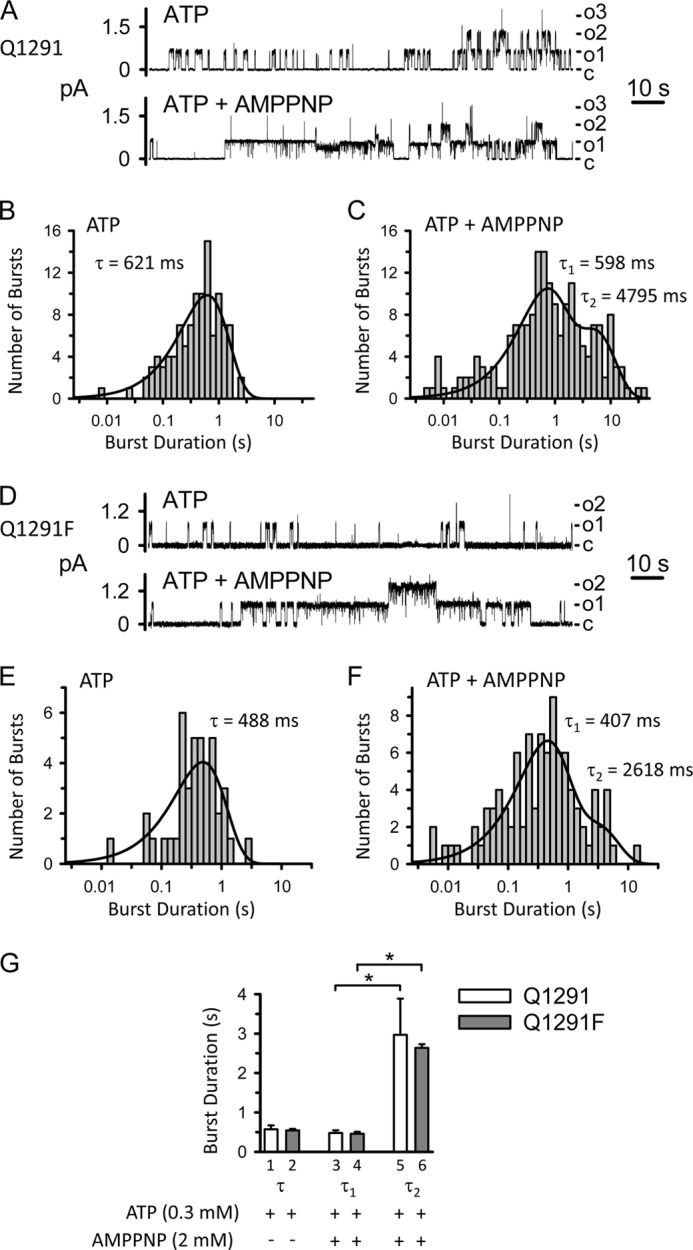
Effect of AMPPNP on wild-type (Q1291; A–C) and Q1291F (D–F) CFTR burst duration. A and D, examples of two 140-s current traces from the same excised membrane patch containing at least three wild-type (A) and two Q1291F (D) CFTR channels before and after adding AMPPNP (2 mm) to the cytosolic surface. ATP (0.3 mm) and PKA catalytic subunit were present throughout the experiments. c, channel closed state; o1, o2, and o3, open states. Holding voltage was −80 mV. For illustration purposes, traces were digitally low pass-filtered at 50 Hz. B, C, E, and F, burst duration histograms of wild-type (B and C) and Q1291F (E and F) CFTR channel activity before (B and E) and after (C and F) adding AMPPNP derived from the experiments shown in A (histograms B and C) and D (histograms E and F). Data were plotted and fit as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Solid lines, superimposed fits of sums of exponential probability functions. In B and E, data were fit to single exponential functions with time constant τ. Fits with two exponential components were not statistically better. In C and F, data were fit to two-component exponential functions (with time constants τ1 and τ2), which fit the data statistically better than single exponential functions. Three exponential components did not fit the data statistically better than two components. Thus, the burst duration distributions indicated two distinct populations of bursts. G, summary data. Each column is the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of 3–4 experiments performed as illustrated in A–F with different membrane patches. Burst duration histograms in the presence of ATP but in the absence of AMPPNP were fit to single exponential functions with time constant τ as illustrated in B and E. When AMPPNP was also present, data were fit to two-component exponential functions with time constants τ1 and τ2 as illustrated in C and F. *, p < 0.05 compared with the results for τ1 (Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA on ranks followed by Dunn's method of multiple comparisons versus control group). The differences between columns 1–4 (one-way ANOVA) and between columns 5 and 6 (Student's t test) are not significant.
