FIGURE 7.
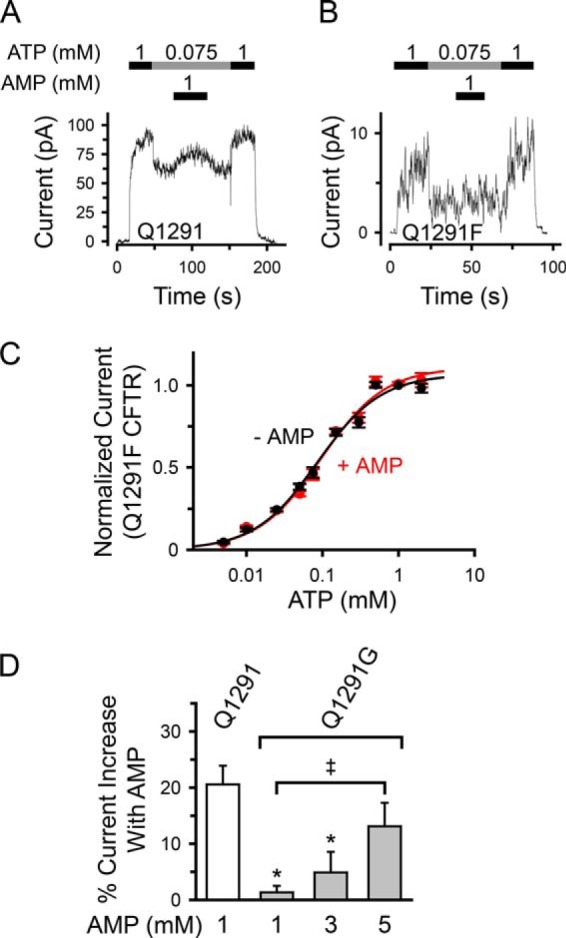
Influence of Gln-1291 mutations on the effect of AMP on CFTR Cl− current. A and B, time courses showing the effect of AMP added at 75 μm ATP on wild-type (Q1291) (A) versus Q1291F (B) CFTR Cl− current. Recordings (100 ms averages) are from excised inside-out membrane patches containing multiple wild-type (A) or Q1291F (B) CFTR channels. ATP and AMP were present during times and at concentrations indicated by bars. ATP was added together with PKA catalytic subunit as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Holding voltage was −40 mV. C, quantitative data showing lack of effect of AMP (1 mm) on ATP-dependent Q1291F CFTR current. Experiments were performed as shown in B. Data are from 15 patches with n ≥ 8 for each ATP concentration. Current measurements in the absence of AMP are the same as shown in Fig. 4 for Q1291F CFTR. All current recordings were normalized to the current obtained with 1 mm ATP in the absence of AMP. Lines are fit to the Hill equation. Data in the absence of AMP were fit using an apparent Km of 87 ± 7 μm, maximum normalized current at high ATP concentrations of 1.07 ± 0.03, and a Hill coefficient of 1.04 ± 0.07. Data in the presence of AMP were fit using an apparent Km of 96 ± 9 μm, maximum normalized current at high ATP concentrations of 1.11 ± 0.03, and a Hill coefficient of 1.03 ± 0.07. D, removal of the Gln-1291 side chain (Q1291G mutation) reduces the potency of AMP to increase CFTR Cl− current. The percentage of current increase with AMP was calculated as the difference between the current at 75 μm ATP before and after adding AMP, divided by the current in the absence of AMP (at 75 μm ATP) and multiplied by 100. Experiments were performed as shown in A. Each column shows the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of 7–13 individual experiments obtained from at least three membrane patches. *, p < 0.05 compared with wild type (Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA on ranks followed by Dunn's method of multiple comparisons versus control group). Double dagger, p < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney rank sum test).
