Fig. 4.
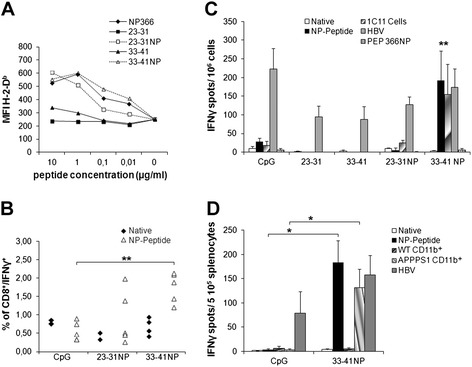
Binding affinities and immunogenicity of Aβ-derived CD8+ candidate epitopes. (a) RMAS cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of native or NP-modified peptides, and cell surface stabilization of H-2-Db was evaluated by FACS. Data are presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of H-2-Db staining. NP366 served as a high-affinity reference peptide. (b) Frequency of IFNγ-producing specific CD8+ T cells in the blood of immunized mice. C57BL/6 mice were vaccinated with NP-modified peptides in CpG/HBV/IFA or with PBS/CpG/HBV/IFA, and animals were bled 14 days later. Percentage of peptide-specific T cells among CD8+ cells in the blood was determined by intracellular IFNγ staining after in vitro restimulation. (c, d) Frequency of Aβ-specific IFNγ-producing splenocytes in immunized mice, as assessed by ELISPOT. (C) C57BL/6 mice were immunized with PBS/CpG/HBV/IFA or the indicated peptides in CpG/HBV/IFA, and 14 days later, spleen cells (106/wells) were restimulated for 18 h with either the matching native or NP peptide, the HBV-derived helper peptide, or NP366 (10 μg/ml). For immunization with PBS/CpG/HBV/IFA, splenocytes were restimulated with each of the native or NP peptides and data were expressed as mean of the two values. Splenocytes were also stimulated with mitomycin-treated 1C11 cells (2 × 104/wells), a neuronal cell line expressing both APP and H-2b MHC-I. Results are presented as numbers of IFN-γ-secreting cells per 106 splenocytes, after subtracting the mean number of spots obtained in the absence of peptide or cells. (D) Splenocytes (2 × 105/wells) of C57BL/6 mice previously immunized with either PBS/CpG/HBV/IFA or 33-41NP mixed in CpG/HBV/IFA were restimulated on day 14 with 33-41NP (10 μg/ml) or CD11b+ microglia (3 × 104/wells) isolated from the brain of WT or APPPS1 mice. Mean ± SEM (three to four mice/group). Results are representative of two independent experiments. Mann–Whitney U test, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01
