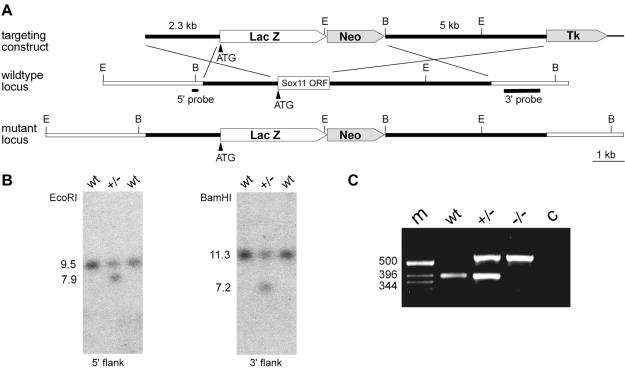
FIG. 1.
Targeted disruption of Sox11 in mice. (A) Schematic representation of the targeting construct (top), the Sox11 wild-type locus (middle), and the mutant locus (bottom). The Sox11 open reading frame is shown as a box, with flanking regions shown as bars. Regions of homology between the wild-type locus and the targeting vector are depicted as black bars, and surrounding genomic regions that are not contained in the targeting construct are depicted as white bars. Plasmid backbone sequences of the targeting construct are indicated by thick lines. Restriction sites for BamHI (B) and EcoRI (E) are shown, as are the locations of the 5′ and 3′ probes and the start codon of the Sox11 gene (ATG). LacZ, gene for β-galactosidase; Neo, neomycin resistance selection cassette; Tk, herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene cassette. (B) Southern blot analysis of DNAs from wild-type (wt) and heterozygous (+/−) ES cells digested with EcoRI for use with the 5′ probe or with BamHI for use with the 3′ probe. The sizes of bands corresponding to the wild-type and targeted alleles are indicated. (C) PCR-based genotyping of wild-type (wt), heterozygous (+/−), and Sox11-deficient (−/−) embryos at 18.5 dpc. The sizes of DNA fragments (in base pairs) in the DNA size marker (m) are indicated to the left of the agarose gel. c, control without added genomic DNA.