FIG. 2.
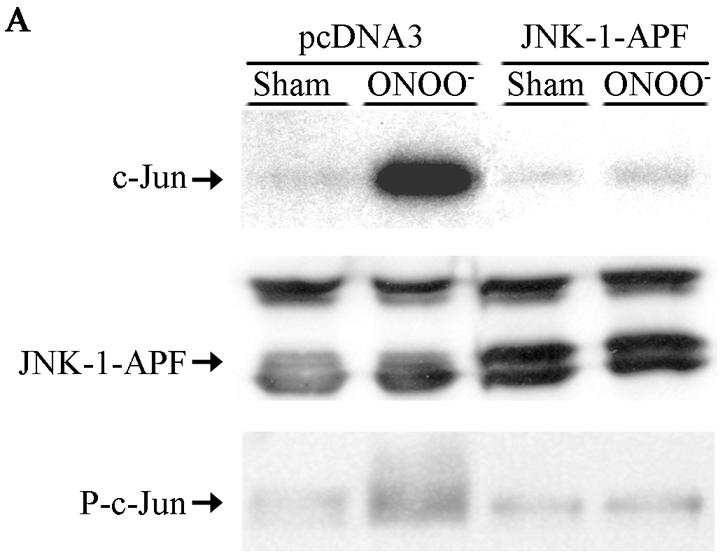
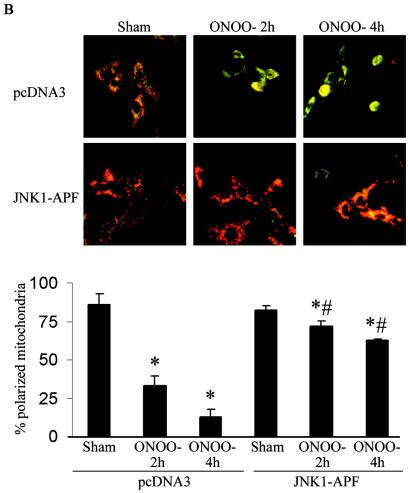
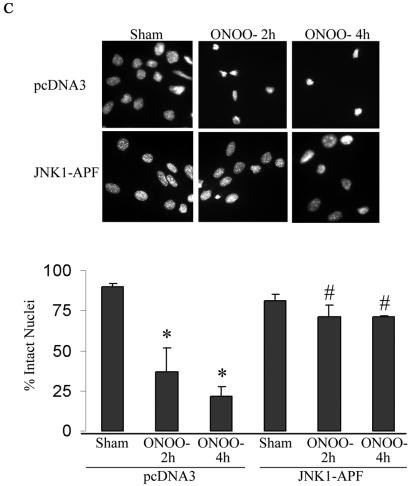
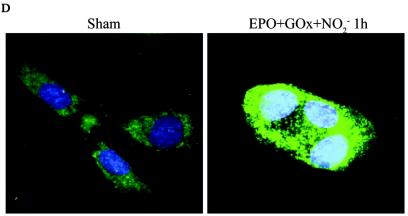
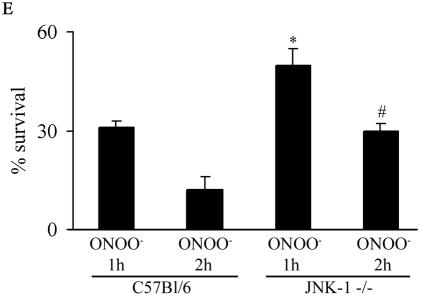
Expression of JNK1-APF inhibits RNS-induced cell death. (A) Assessment of JNK activation and c-Jun phosphorylation in pcDNA3 or JNK1-APF transfected cell pools. Cells were treated with 200 μM ONOO− for 2 h for assessment of JNK activation in an in vitro kinase assay (top) or c-Jun phosphorylation by Western blotting (bottom). (Middle panel) Western blotting for JNK1. The expression of JNK1-APF is indicated. pcDNA3 or JNK1-APF cells grown on glass coverslips were treated with 200 μM ONOO− for the indicated times for the assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential (B) or nuclear condensation (C). Mitochondrial membrane potential was determined by incubation with 5-μg/ml JC-1. Polarized mitochondria are visualized by punctate red staining, whereas depolarized mitochondria are visualized by their diffuse green staining. Cells were counted in five random fields, and data are expressed as a percentage of polarized cells. Nuclear condensation was determined after staining of cells with 5-μg/ml Hoechst. Cells were counted in five random fields, and data are expressed as a percentage of cells containing intact nuclei. Results are expressed as means ± standard error. *, P < 0.05 compared to sham controls; #, P < 0.05 compared to pcDNA3 vector controls (analysis of variance). (D) Assessment of AIF nuclear localization in cells exposed to 50 nM EPO in the presence of 15-mU/ml glucose oxidase (GO) and 100 μM sodium nitrite (NO2−) for 4 h. Nuclear presence of AIF (green) was confirmed via confocal microscopy and colocalization with propidium iodide (blue). (E) Assessment of viability of C57BL/6 or JNK1−/− lung fibroblasts exposed to 200 μM ONOO−, using the MTT assay. Data are expressed as percent survival compared to sham controls. *, P < 0.05 (analysis of variance) compared to C57BL/6-derived fibroblasts exposed to ONOO− for 1 h; #, P < 0.05 (analysis of variance) compared to C57BL/6-derived fibroblasts exposed to ONOO− for 2 h.