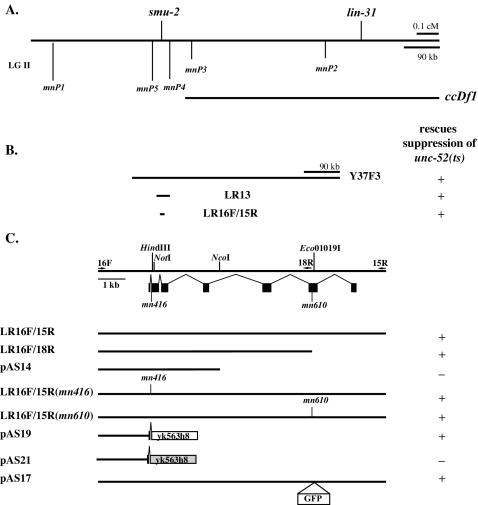
FIG. 3.
Mapping and cloning smu-2. The scales in panels A and B are identical. (A) Genetic map position of smu-2 with respect to the lin-31 gene and DNA sequence dimorphisms between strains N2 and RC301, which were used in mapping. The left end point of ccDf1, representing a deficiency that deletes lin-31 and complements smu-2, was mapped between dimorphisms mnP3 and mnP4. (B and C) Transformation rescue data for smu-2 with YAC DNA and long-range PCR products. + indicates that at least one line that rescued smu-2, as assayed by reversal of unc-52 suppression, was obtained; − indicates that several lines that did not rescue smu-2 were obtained. (C) The exon-intron structure of smu-2 is indicated below the restriction map. Arrows, locations of primers used to generate long-range PCR products. Eco01019I, NotI, and HindIII restriction sites used to construct pAS17, pAS19, and pAS21, respectively, are indicated. yk563h8 is a full-length smu-2 cDNA. pAS21 has a frameshift mutation introduced at the HindIII site (light gray box). The placement of the GFP gene for plasmid pAS17 is shown. smu-2(mn416) has a point mutation located at the 3′ splice site of intron 1. smu-2(mn610) has a single base pair deletion in the middle of exon 6. LR16F/15R(mn416) and LR16F/15R(mn610) are PCR products that were generated from genomic DNA made from the respective smu-2 mutants.